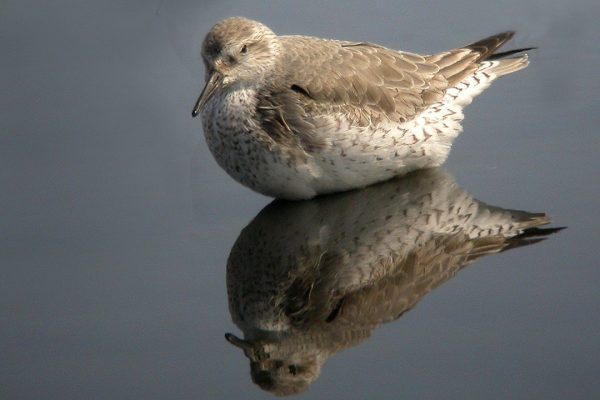
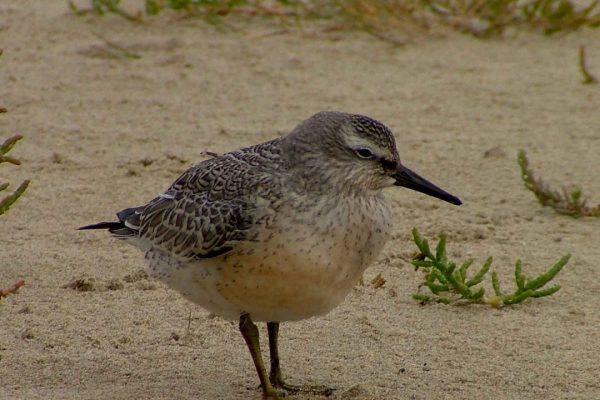
Knot
| Irish Name: | Cnota |
| Scientific name: | Calidris canutus |
| Bird Family: | Waders |
red
Conservation status
Conservation status
Status
Winter visitor from northern Greenland and from the Queen Elizabeth Islands of high Arctic Canada west to Prince Patrick Island. Most occur between October & February.
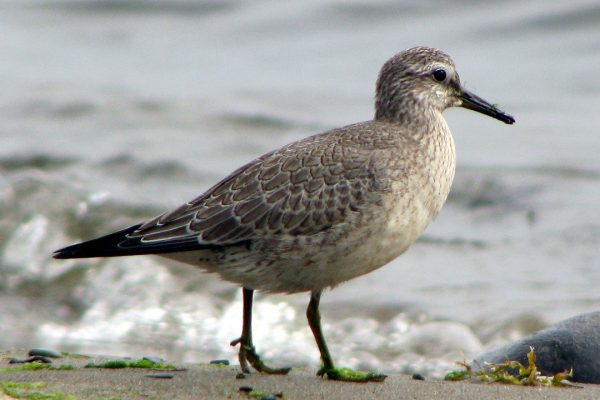
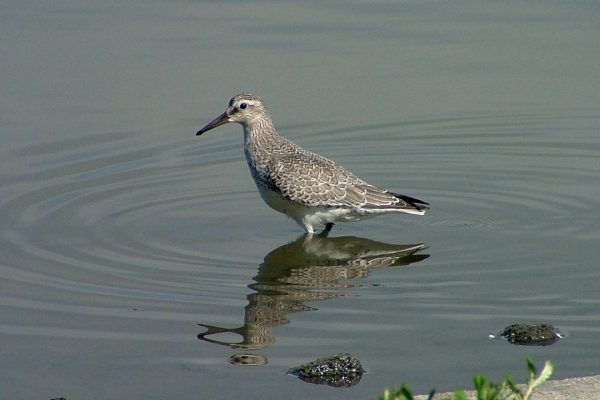
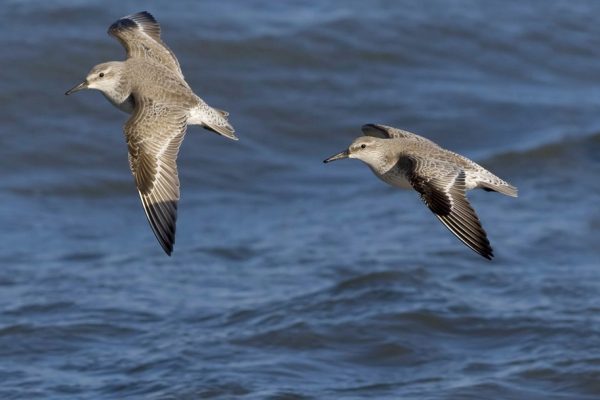
Identification
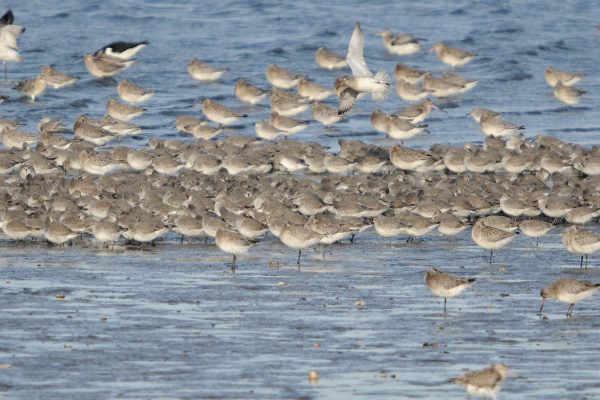
Short-legged plump wader, larger than Dunlin. Fairly non-descript grey plumage, juveniles in autumn show warm buff wash on breast and underside. Occasional brick-red summer plumaged birds occur on passage. Legs greyish-green. Bill straight, of similar length to head. Long-winged appearance in flight, with thin white wing-bar and pale-grey rump patch. More likely to be seen in very large flocks than singly or small groups.
Voice
Soft, nasal 'whet-whet'.
Diet
Feed predominantly on bivalve mussels and crustaceans. Macoma balthica is the preferred prey and Hydrobia ulvae, Mytilus edulis and Cerastoderma edule are selected when Macoma sp. is absent close to the surface of the sediment. Knots possess large numbers of sensors on their bills and that they are able to detect hard-shelled prey even when buried beyond the reach of their bills.
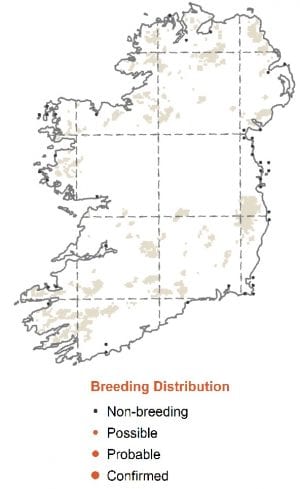
Breeding
Breed at low density, and often close to the coast, nesting on well concealed and sparsely vegetated gravel and rocky slopes.
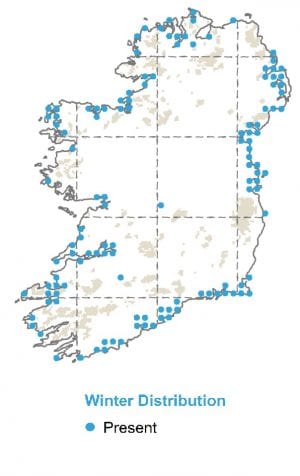
Wintering
The wintering distribution is entirely coastal, and their preferred habitat mostly includes estuarine sites with extensive areas of muddy sand. They occur mostly in large flocks and on fewer estuaries than other wader species.
Monitored by
Blog posts about this bird
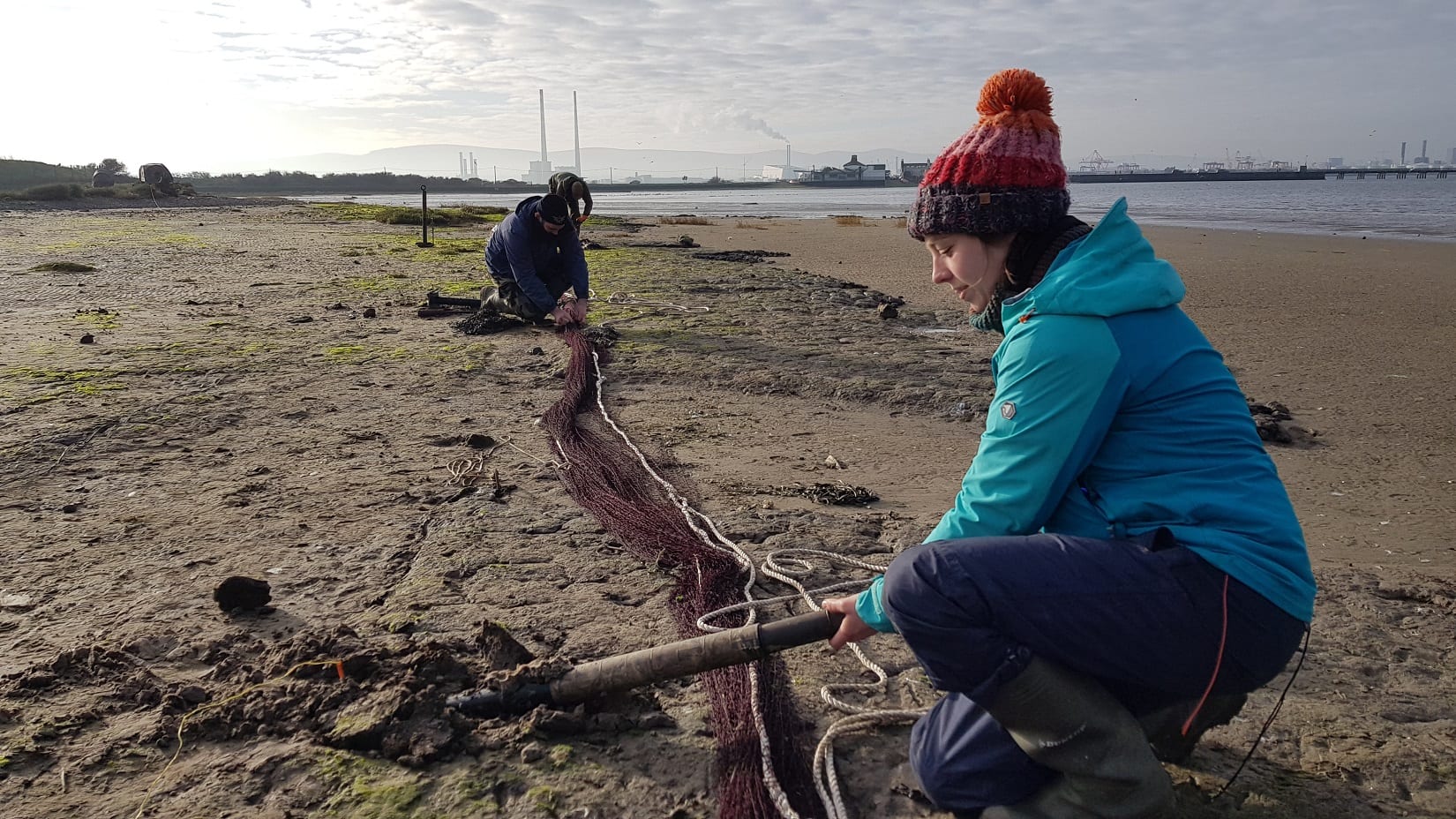

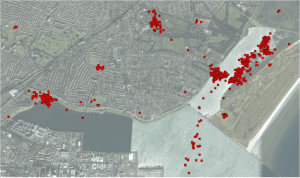
Starting 2020 with a (literal) BANG!! Catching and colour-ringing waders in Dublin Bay
In January 2020, the Dublin Bay Birds Project Team put in a huge effort to fit colour-rings (safely, and under license) to the legs of a portion of the wintering waders in Dublin Bay. Over four days and nights, we caught and ringed 235 waders of 6 species, with 23 ‘re-trapped’ birds, two of which were Icelandic-ringed Oystercatchers! The precise tally is 199 Oystercatchers, 23 Black-tailed Godwits, 5 Redshank, 4 Dunlin, 3 Curlew, and 1 Knot.


We used a highly specialised technique called ‘cannon-netting’ (firing a large net outwards using weighted projectiles propelled from cannons) to capture the birds. To do this, we 

Essentially, the fitting of colour-rings to the legs of these wintering waders in Dublin and the subsequent reading and reporting of them (and similarly the fitting of small GPS-devices to birds) is 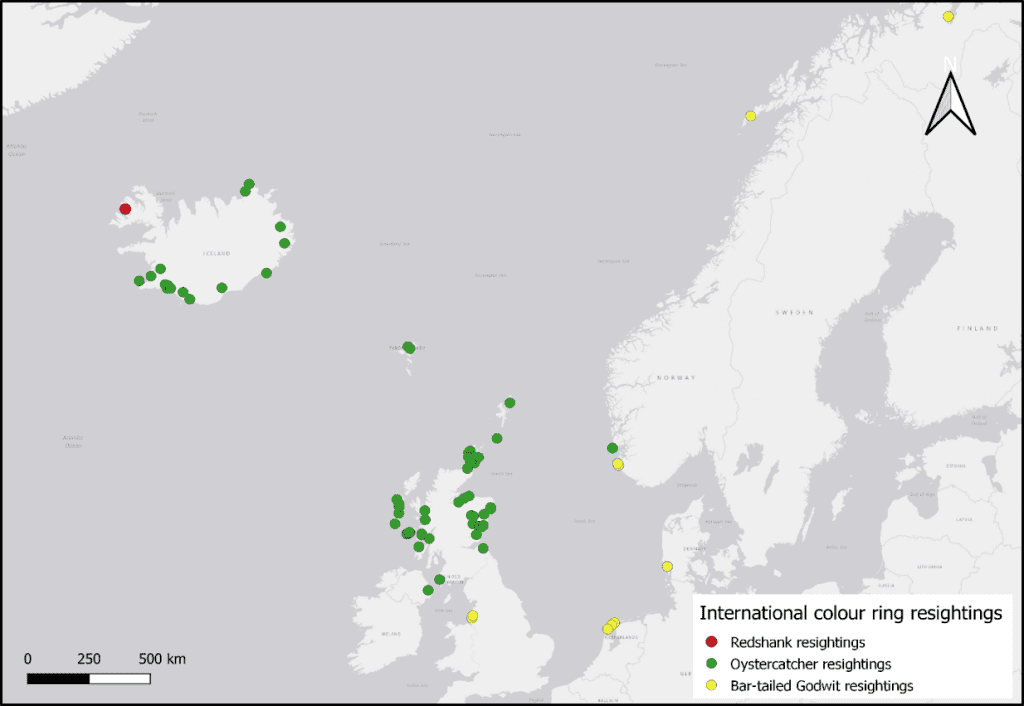
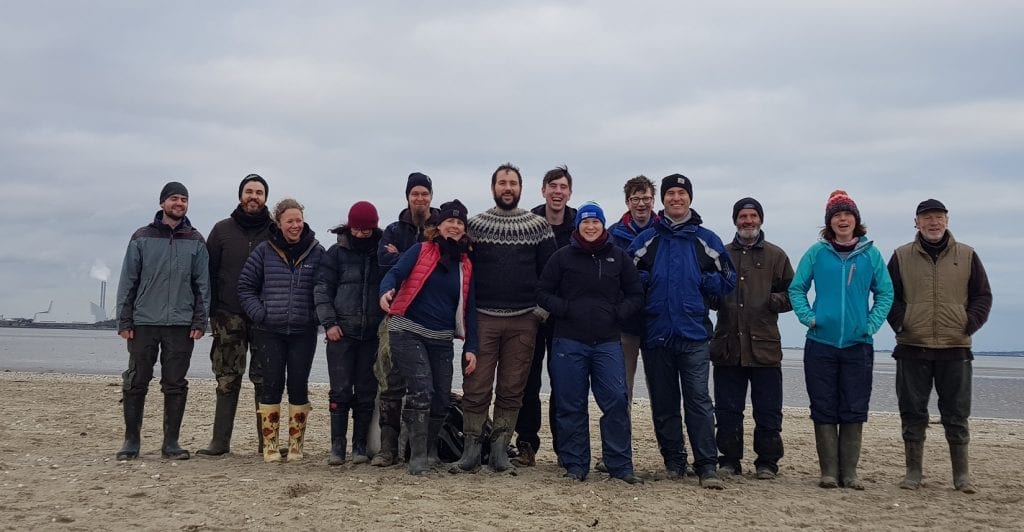

Now the work is to go out and look for all of these colour-ringed birds, read those inscriptions and submit them to us!
Submit your resightings HERE!
The Dublin Bay Birds Project is very lucky to be supported by Dublin Port Company who keenly recognise the value of this work and the data it generates.

This work was carried out under license from the National Parks and Wildlife Service and the British Trust for Ornithology.