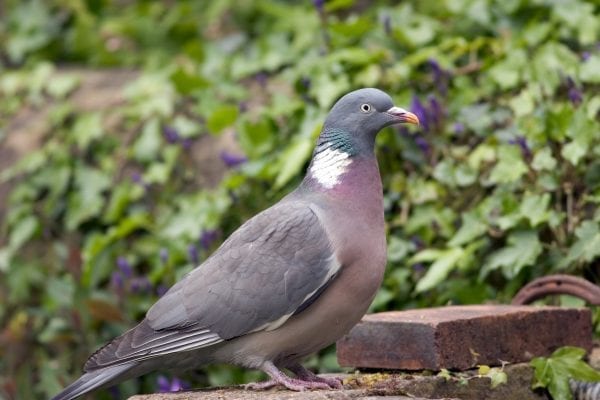
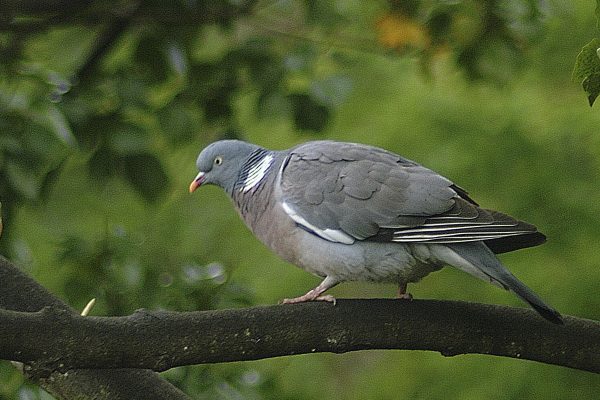
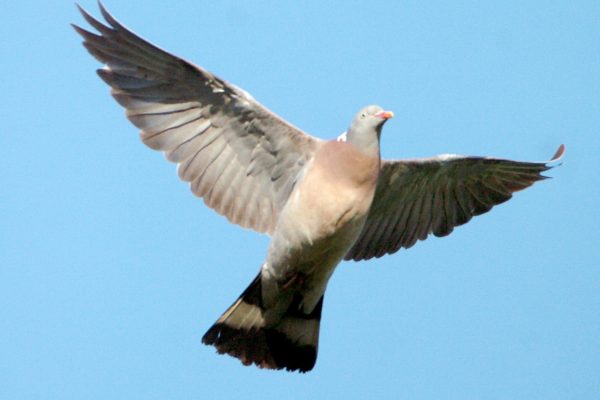
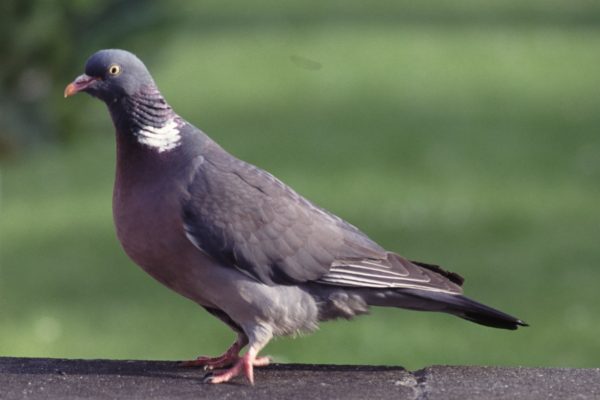
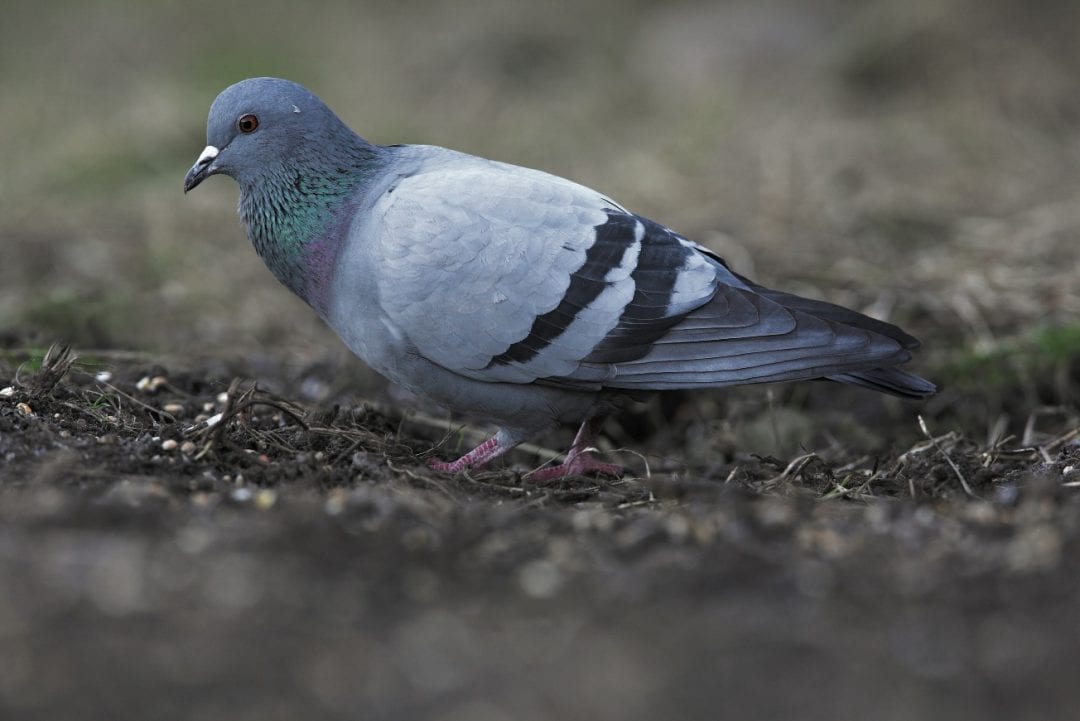
Woodpigeon
| Irish Name: | Colm coille |
| Scientific name: | Columba palumbus |
| Bird Family: | Pigeons & Doves |
green
Conservation status
Conservation status
Status
Resident, with birds joined by large numbers of immigrants from Britain and the continent in the winter. One of Ireland's top 20 most widespread garden birds.
Identification
The largest of the pigeons in Ireland with a proportionally long tail and small head. A full breast. Easily identified in flight by large white wing bands traversing the upper wing. White and green patches on the side of the neck. In the breeding season they are conspicuous in upward-soaring display flights which end in wing clapping.
Voice
Clattering wing noise on take off. The song consists of a hollow three noted cooing - "whooo who huhu".
Diet
Mainly plant material, green leaves, seeds, berries, buds, flowers and root crops.
Breeding
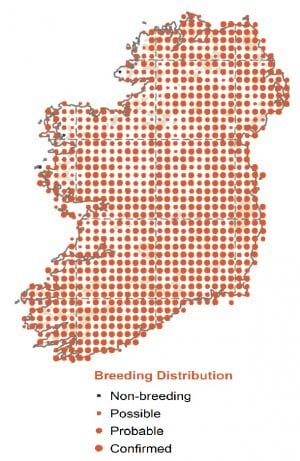
A widespread breeder, found throughout Ireland, only in the higher hills and mountains are they absent. Originally a woodland bird, it is also found in parks and gardens, even in town centres where they have become quite tame. A very adaptable bird, it has been recorded breeding in heather and stunted bushes in the windswept west of the country.
Wintering
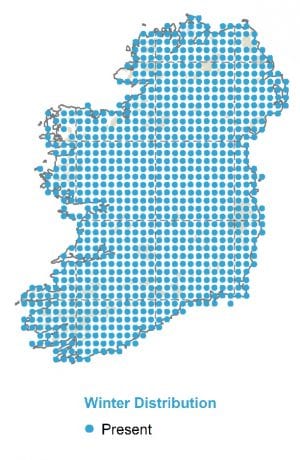
The Irish population is boosted by wintering birds from Continental Europe. Flocks of several hundred to a thousand may gather in good feeding areas.
Monitored by
Blog posts about this bird

BirdWatch Ireland Calls for Public Participation in Critical Bird Survey Starting November 25th
BirdWatch Ireland is calling on people across the country to help monitor the health of the country’s bird populations by counting the birds visiting their garden over the winter.
Ireland’s longest-running and most popular citizen science survey, the Irish Garden Bird Survey, will commence on Monday, November 25th and run until the end of February. Taking part is free and simple, yet impactful, as all participants contribute to a crucial body of data that will help to inform monitoring and research into bird populations and environmental change.
Last year’s survey, which saw over 1,600 households across the country participating, revealed the Robin as Ireland’s top garden bird once again, present in 96% of gardens. Blackbird and Blue Tit followed in second and third place, occurring in 94% and 91% of gardens respectively. However, all three species appeared in fewer gardens than at any point in the last thirty years due to the mild winter weather conditions, which reduced birds’ need for garden feeders.
Of the top 30 species seen in Irish gardens last winter, 25 occurred in a lower percentage of gardens than the previous winter.







Blue Tit. Photo: Michael Finn.
“We often get emails from people early in the winter wondering where their garden birds are, but last winter people all over the country were commenting on how quiet their gardens were,” said Brian Burke, coordinator of the Irish Garden Bird Survey. “This week we’re seeing very cold conditions across the country, and that’s definitely driving more birds into gardens at the moment, so it’ll be interesting to see what the coming weeks bring. The more people who do the survey, the more we can learn about these sorts of links between climate, birds and our environment.”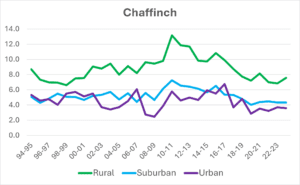
Average Chaffinch numbers per garden show that they occur in greater flock sizes in rural gardens than urban or suburban ones.
Other species including Chaffinch, Coal Tit and Jackdaw were at their lowest occurrence in 30 years, while Song Thrush and Pied Wagtail showed a huge drop of 12% since the previous winter. One species, the Siskin, bucked this trend, occurring in 41% of gardens compared to 26% the previous year. This is largely due to their reliance on alder, birch, spruce and pine tree seeds as a food source. Considering the cyclical nature of seed supply, such peaks in Siskin numbers are expected every three years or so. They tend to occur in relatively few gardens in December, increasing in January, and becoming much more common throughout February. Similar mid-winter increases were seen with Redpoll and Long-tailed Tit, amongst other species.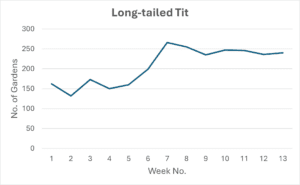
Long-tailed Tit occurrence in gardens increased greatly after the first week of January (Week 6) and remained high until the end of February.
While it was anticipated that Greenfinch would experience declines due to the impact of the deadly Trichomoniasis condition on the species, it was one of very few species with a stable trend and virtually no change from the previous winter. Greenfinch have occurred in 47-48% of gardens in each of the last three winters, which may indicate that their rapid declines have stabilised. The species is currently on the Amber list as a species of medium-level conservation concern. As usual, there are clear differences in the birds visiting gardens across the country. Notable differences in Ulster include Blackbird being the most widespread species, Goldfinch not featuring in the top 10 (12th), and it being the only province with either Jackdaw or Song Thrush in the top 10. Out west in Connaught, Coal Tit and Wren came in 9th and Starling only in 13th. Leinster was once again the only region to feature Woodpigeon in the top 10. The top 10 in Munster was very similar to the national rankings, though notably, the Rook was the 11th most common species there, much higher than elsewhere. As a conservation charity with a small team, BirdWatch Ireland is reliant on members of the public to help gather vital data about Ireland’s many bird species. In addition to contributing valuable information, participants often enhance their bird identification skills and gain insights into the journeys these birds undertake. Indeed, some of last year’s participants reported ringed birds that visited their gardens including a Goldfinch discovered in Tipperary that was originally ringed in Maine-et-Loire in France, and a Redwing found in Carlow that was ringed at Sandwich Bay Bird Observatory in Kent, England.
Goldfinch. Photo: Kevin Murphy.
Taking part in the Irish Garden Bird Survey is a win-win for science and for individual participants and this year, BirdWatch Ireland hopes to encourage even more people to take part. All you need to get involved is a little bit of time each week to watch your garden birds, access to a garden or any outdoor space such as a community garden or school grounds, and a sense of curiosity. The Irish Garden Bird Survey is once again sponsored by Ballymaloe, whose support in recent years has helped ensure the survey has gone from strength to strength, improving monitoring at national level and allowing for greater focus on conservation issues facing individual species. Commenting on their ongoing support for the survey, a Ballymaloe spokesperson said: "United in our commitment to the environment and inspired by the legacy of our forefather, Ivan Allen, Ballymaloe businesses as a group proudly sponsor BirdWatch Ireland's annual Irish Garden Bird Survey. Mr Ivan Allen, the husband of Myrtle Allen and a devoted lover of birdlife, cherished the natural habitat around Ballymaloe House, and practised sustainable farming way ahead of his time. In his memory, our collective support for the Irish Bird Survey reflects our ongoing celebration of Mr Allen's passion for birdlife and commitment to conservation. Together Ballymaloe House Hotel, the Ballymaloe Cookery School and Ballymaloe Foods are honoured to contribute towards supporting the preservation of Irish birdlife via BirdWatch Ireland's important national Irish Garden Bird Survey initiative in his name. We encourage as many households as possible to get involved, every entry helps BirdWatch Ireland protect birdlife on the island of Ireland." To learn more about the survey and to get involved, see here: https://birdwatchireland.ie/our-work/surveys-research/research-surveys/irish-garden-bird-survey/.


From early birds to late bloomers: exploring the nesting patterns of birds
Every March 1st, reminders of the annual hedge-cutting ban are disseminated and rolling in behind them are jokes and comments alluding to birds and their strict schedules.
Of course, birds don’t maintain annual calendars like you or I. If they did, things would be much more clear-cut! However, their behaviour including nesting and migration is tied to seasonal shifts. The rising temperatures and longer hours of daylight ushered in by spring prompt the beginning of nesting season for wild birds. The hedge-cutting ban is in place to prevent the destruction or disturbance of their nesting sites.
Blackbird. Photo: Jerry Cassidy.
Springing into nesting season
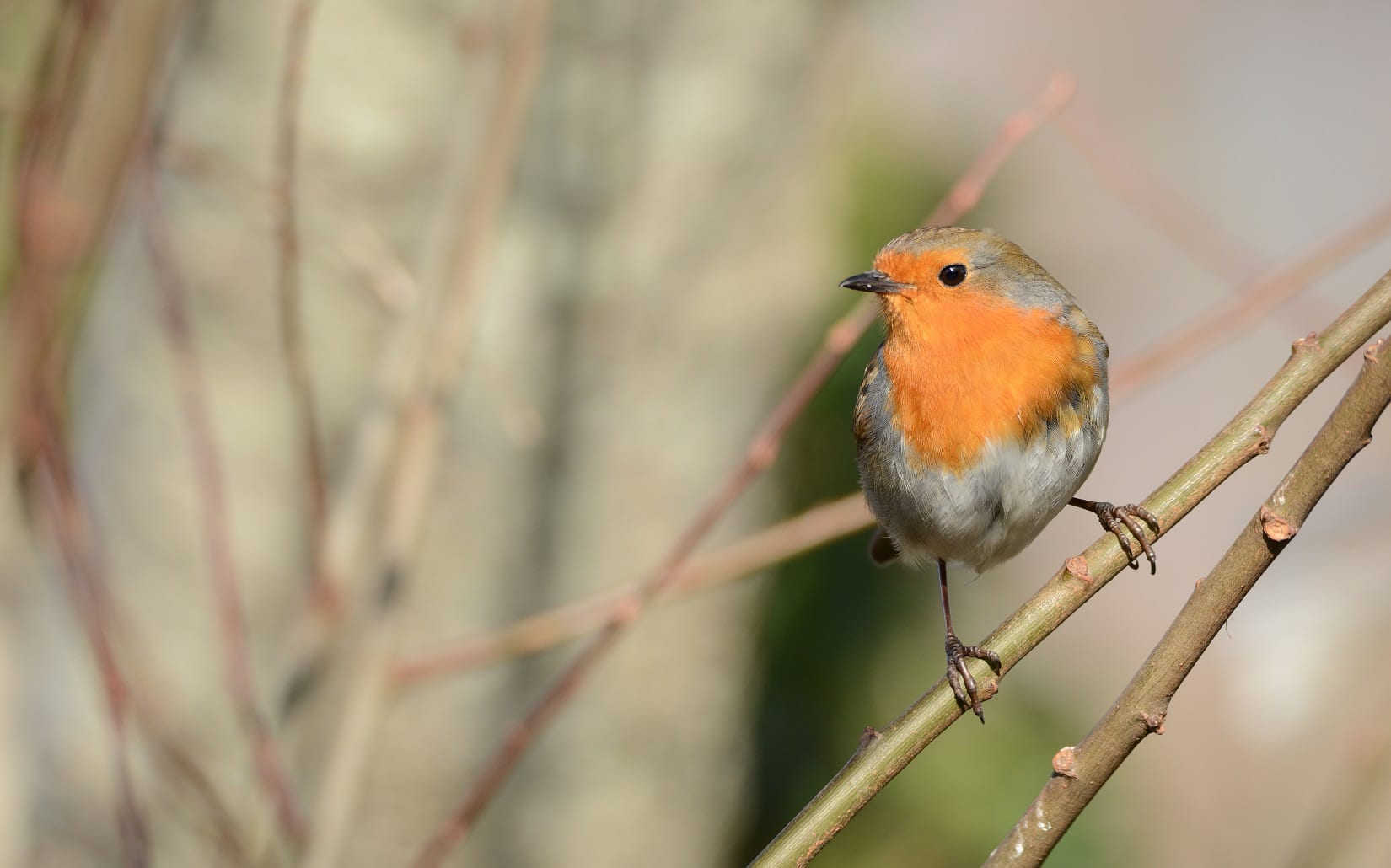
At present, the cut-off point for hedge-cutting is informed by the best available data. With the subject understudied here in Ireland, much of what we know about nesting is derived from UK data, specifically, the British Trust for Ornithology’s Nest Record Scheme (NRS). Based on the information we have, March 1st is considered an appropriate time to stop hedge-cutting for most nesting birds. However, in reality, it is likely that the nesting season begins much earlier in Ireland than in the UK owing to our milder climate. We also know that some birds nest earlier in the season. Data from the BTO Nest Record Scheme shows that some species such as Blackbird and Robin can nest much earlier than March 1st, with records of both species nesting in January (or even December) becoming annual. As the ongoing climate crisis drives global temperatures up, it is possible that “early nesting” will become the norm, rather than the exception. Indeed, a US study published in the Journal of Animal Ecology showed that one-third of 72 bird species studied are now nesting significantly earlier than they did historically. These species, which include Blue Jays and Field Sparrows, are now laying their eggs on average 25 days earlier than 100 years ago.Robin. Photo: Brian Burke
Late-nesting birds
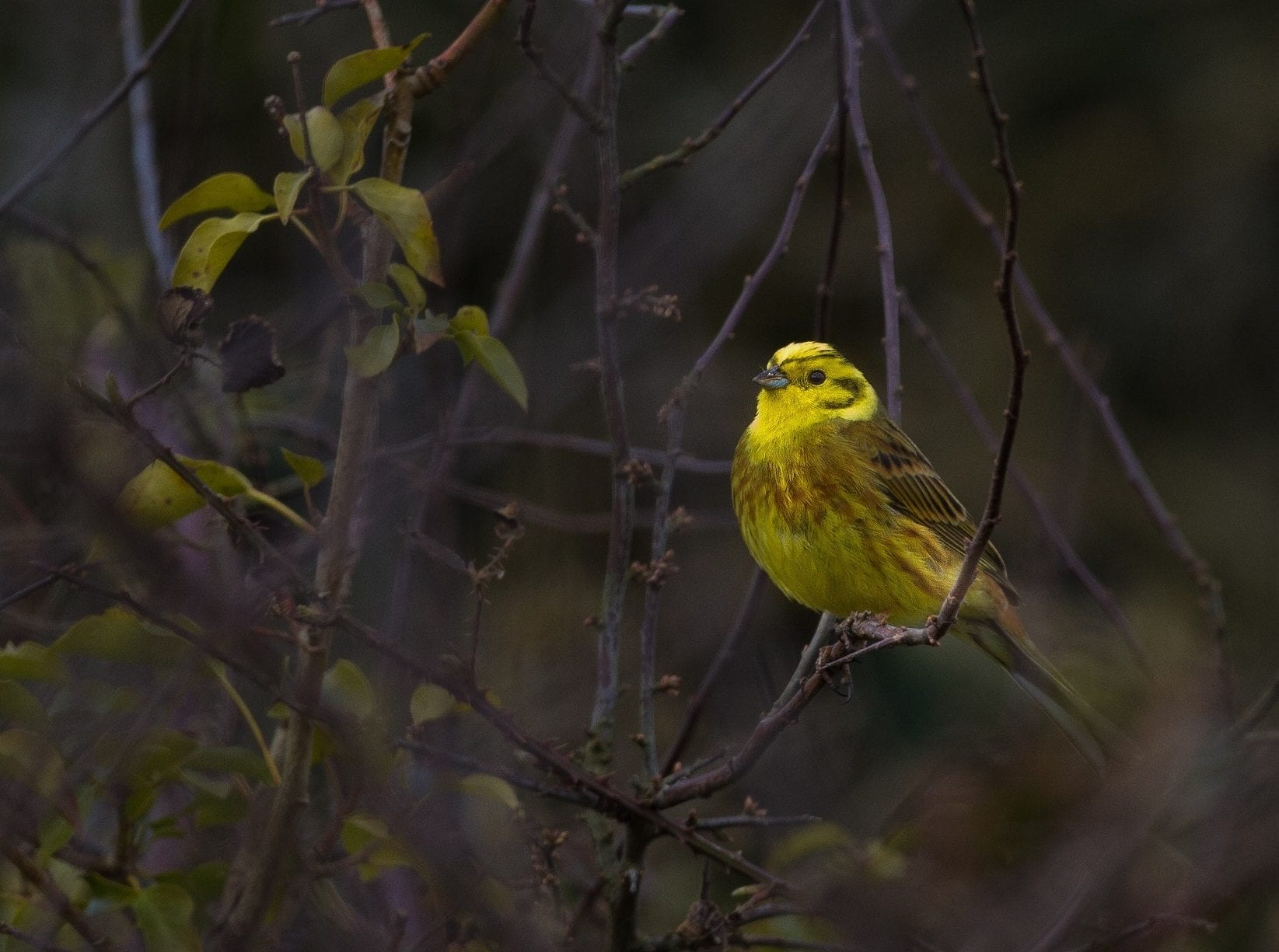
While August 31 currently marks the end of the ban on hedge-cutting, that is not to say that all chicks will have fledged by this date. Once again, things are a bit more complicated than that. Initiated in 2017, BirdWatch Ireland’s Late-nesting Bird Project collected information about Yellowhammer and other bird species such as Goldfinch, Greenfinch and Blackbird that may be nesting in hedgerows in August and September. A large pool of recorders in 20 counties were asked to note breeding evidence of hedgerow nesting birds in August and September. In order to avoid disturbance, they were asked to note breeding evidence as opposed to actively searching for nests. Breeding evidence includes a singing male, a bird carrying nest material, an adult carrying a fecal sac or food, agitated behaviour, and more. The results showed that Yellowhammer in particular nests well into August and September. The Yellowhammer is a Red-listed species of Conservation Concern, meaning that it is at the highest level of conservation concern and in danger of extinction. Failure to acknowledge and protect late-nesting species by adhering to the current legislation could lead to the quiet chipping away of what remains of this wonderful species. Yellowhammer were not the only species shown to nest into the autumn months. The next most regularly recorded species during August and September were Goldfinch (19), Greenfinch (16), Woodpigeon (10) and Blackbird (9). Once again, we must not lose sight of the impact of climate change. As temperatures increase, it is possible that more birds will nest late into the year.Yellowhammer. Photo: Colum Clarke.