Great Spotted Woodpecker
| Irish Name: | Mórchnagaire breac |
| Scientific name: | Dendrocopus major |
| Bird Family: | Woodpeckers |
green
Conservation status
Conservation status
Status
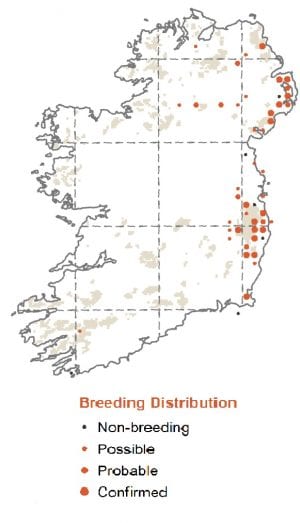
Colonist to broadleaf forests in eastern Ireland since 2005, now gradually expanding its range to other parts of the country.
Identification
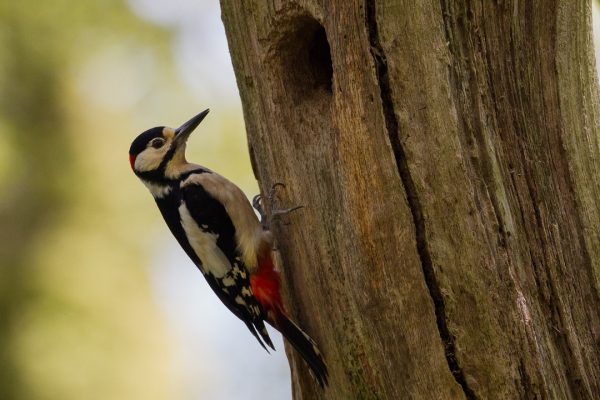
About the same size as Mistle Thrush. A distinctive black and white bird when seen well. The face, throat and underparts are white, while the back, rump and tail are black. Also has a large white patch at the base of the wings, while the vent is pale red. In flight, the wings are mainly black, with obvious rows of spotting on the primaries and secondaries. Adult male Great Spotted Woodpeckers are identifiable by a small red patch on the back of the head. Adult females have a black nape and crown.
Voice
The most frequently heard call is a loud "kick", when agitated given in a continuous series. Does not sing, but has distinctive drumming display from early spring onwards. Drums last between 1 and 2 seconds.
Diet
Feeds on insects found in wood, as well as pine cones in autumn. During the breeding season, may also take eggs and chicks of other birds. Will visit garden bird tables in suburban areas.
Breeding
A scarce but increasing breeder in Ireland, usually in oak woodlands with some coniferous woods nearby. A common species in Britain and Continental Europe and frequently visits bird feeders in gardens. Breeds in nesting cavities which it excavates in decaying wood.
Wintering
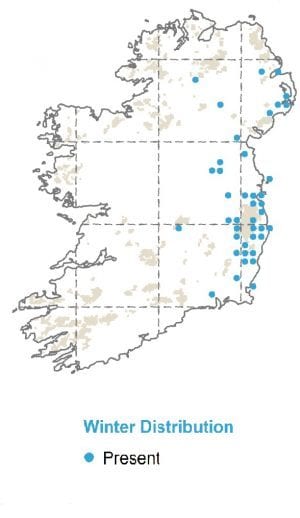
Great Spotted Woodpeckers remain on their territory during the winter. Young birds move to new territories in autumn
Monitored by
Countryside Bird Survey, Great Spotted Woodpecker Survey and BirdTrack.
Blog posts about this bird

35th Irish Garden Bird Survey is ready to take flight
Birds inject a huge amount of joy into our lives, creating the soundtrack to spring mornings and brightening up our gardens on otherwise drab winter days.
As we approach what is widely considered the “season of giving”, one surefire way to give back to the birds for all that they do for us is to participate in this year’s Irish Garden Bird Survey – the most popular and longest-running citizen science survey in Ireland.

 Last year, the Robin came out on top again in Irish gardens having been seen in 99% of gardens, though were pushed to second place by the Blackbird in counties Wicklow, Offaly, Kildare and Antrim. The mild weather over the majority of last winter meant that many species were similarly widespread as in previous winters. In addition to Robin and Blackbird, Blue Tits and Magpies both occurred in over 90% of Irish gardens, while Great Tit, Chaffinch, House Sparrow and Goldfinch were in over 80% of gardens. For House Sparrow, it was their second-best year on record, likely due to a bumper breeding season. The species is on the ‘Amber list’ of Birds of Conservation Concern, so this positive trend is to be welcomed.
Though the winter weather was mostly mild, there were a few short spells of snow which drove birds into gardens in higher numbers. The first species affected by this are often the birds in the thrush family, including our resident Song Thrush and Mistle Thrush, migrant Redwing from Iceland and Fieldfare from Scandinavia.
“Despite the temperatures being mild overall, we seem to be getting more storms and multiple short snowy spells in recent years, and these can be enough to deplete birds’ fat reserves and put them under real pressure. Song Thrush occurred in an extra 12% of gardens last year owing to the snowy weather” said Burke. “So, these are the times when your garden birds really need you to provide food and water, and if you can put these out a few days before any snow hits then you’re giving the birds a chance to realise it’s there, so they know exactly where to go when the ground freezes over.”
Last year, the Robin came out on top again in Irish gardens having been seen in 99% of gardens, though were pushed to second place by the Blackbird in counties Wicklow, Offaly, Kildare and Antrim. The mild weather over the majority of last winter meant that many species were similarly widespread as in previous winters. In addition to Robin and Blackbird, Blue Tits and Magpies both occurred in over 90% of Irish gardens, while Great Tit, Chaffinch, House Sparrow and Goldfinch were in over 80% of gardens. For House Sparrow, it was their second-best year on record, likely due to a bumper breeding season. The species is on the ‘Amber list’ of Birds of Conservation Concern, so this positive trend is to be welcomed.
Though the winter weather was mostly mild, there were a few short spells of snow which drove birds into gardens in higher numbers. The first species affected by this are often the birds in the thrush family, including our resident Song Thrush and Mistle Thrush, migrant Redwing from Iceland and Fieldfare from Scandinavia.
“Despite the temperatures being mild overall, we seem to be getting more storms and multiple short snowy spells in recent years, and these can be enough to deplete birds’ fat reserves and put them under real pressure. Song Thrush occurred in an extra 12% of gardens last year owing to the snowy weather” said Burke. “So, these are the times when your garden birds really need you to provide food and water, and if you can put these out a few days before any snow hits then you’re giving the birds a chance to realise it’s there, so they know exactly where to go when the ground freezes over.”
 Some very rare species were spotted in small numbers in Ireland last winter such as Bramblings, Lesser Whitethroats, Black Redstarts, Snow Buntings and Ring-necked Parakeets.
Some very rare species were spotted in small numbers in Ireland last winter such as Bramblings, Lesser Whitethroats, Black Redstarts, Snow Buntings and Ring-necked Parakeets.
35 years of the Irish Garden Bird Survey
Now in its 35th year, the Irish Garden Bird Survey grants people across the country the opportunity to serve as our eyes on the ground by observing and recording birds in their gardens, on school grounds, on their balconies, or within any other space they enjoy daily. All of this information gives us insight into how different species are faring and, in turn, helps us to identify current threats and future conservation priorities.
Blue Tit. Photo: Brian Burke.
The Irish Garden Bird Survey is perhaps our most simple and inclusive survey, one in which people of all ages, backgrounds and experience levels can play their part. In fact, it is so simple that, whether or not you have heard of the Irish Garden Bird Survey, it is likely that you are already doing the work. “The Irish Garden Bird Survey is something you can do with a cup of tea looking out the window. You can do it as you're washing the dishes or filling the kettle. People are always watching their garden birds during the winter anyway. That’s when the garden bird numbers peak. The birds are driven to gardens to look for food and people might be inside a lot more because the weather isn’t as good,” says Coordinator of the Irish Garden Bird Survey, Brian Burke. “As we always tell people, you are probably doing this anyway. We just are asking you to go that extra step by writing down and sending us what you see.” While participating in the Irish Garden Bird Survey does not take a lot of time or effort, the impact of the data collected by participants over the past 35 years has been huge. Thanks to them, we now know that Robins, Blackbirds and Blue Tits are the most common garden bird species in Ireland. We know that species such as Great Spotted Woodpecker are on the rise. We know that the breeding Greenfinch numbers have plummeted by 48 per cent in recent years, a loss that can be almost entirely linked to trichomoniasis – a fatal disease caused by a microscopic parasite which predominantly affects finches.2022/ 2023 Irish Garden Bird Survey Results
While there is some consistency in terms of what species are most common, cold winter weather, autumn food supplies, and the success of the summer breeding season just gone all play a part in what birds arrive in Irish gardens at this time of year. Last year, the Robin came out on top again in Irish gardens having been seen in 99% of gardens, though were pushed to second place by the Blackbird in counties Wicklow, Offaly, Kildare and Antrim. The mild weather over the majority of last winter meant that many species were similarly widespread as in previous winters. In addition to Robin and Blackbird, Blue Tits and Magpies both occurred in over 90% of Irish gardens, while Great Tit, Chaffinch, House Sparrow and Goldfinch were in over 80% of gardens. For House Sparrow, it was their second-best year on record, likely due to a bumper breeding season. The species is on the ‘Amber list’ of Birds of Conservation Concern, so this positive trend is to be welcomed.
Though the winter weather was mostly mild, there were a few short spells of snow which drove birds into gardens in higher numbers. The first species affected by this are often the birds in the thrush family, including our resident Song Thrush and Mistle Thrush, migrant Redwing from Iceland and Fieldfare from Scandinavia.
“Despite the temperatures being mild overall, we seem to be getting more storms and multiple short snowy spells in recent years, and these can be enough to deplete birds’ fat reserves and put them under real pressure. Song Thrush occurred in an extra 12% of gardens last year owing to the snowy weather” said Burke. “So, these are the times when your garden birds really need you to provide food and water, and if you can put these out a few days before any snow hits then you’re giving the birds a chance to realise it’s there, so they know exactly where to go when the ground freezes over.”
Last year, the Robin came out on top again in Irish gardens having been seen in 99% of gardens, though were pushed to second place by the Blackbird in counties Wicklow, Offaly, Kildare and Antrim. The mild weather over the majority of last winter meant that many species were similarly widespread as in previous winters. In addition to Robin and Blackbird, Blue Tits and Magpies both occurred in over 90% of Irish gardens, while Great Tit, Chaffinch, House Sparrow and Goldfinch were in over 80% of gardens. For House Sparrow, it was their second-best year on record, likely due to a bumper breeding season. The species is on the ‘Amber list’ of Birds of Conservation Concern, so this positive trend is to be welcomed.
Though the winter weather was mostly mild, there were a few short spells of snow which drove birds into gardens in higher numbers. The first species affected by this are often the birds in the thrush family, including our resident Song Thrush and Mistle Thrush, migrant Redwing from Iceland and Fieldfare from Scandinavia.
“Despite the temperatures being mild overall, we seem to be getting more storms and multiple short snowy spells in recent years, and these can be enough to deplete birds’ fat reserves and put them under real pressure. Song Thrush occurred in an extra 12% of gardens last year owing to the snowy weather” said Burke. “So, these are the times when your garden birds really need you to provide food and water, and if you can put these out a few days before any snow hits then you’re giving the birds a chance to realise it’s there, so they know exactly where to go when the ground freezes over.”
 Some very rare species were spotted in small numbers in Ireland last winter such as Bramblings, Lesser Whitethroats, Black Redstarts, Snow Buntings and Ring-necked Parakeets.
Some very rare species were spotted in small numbers in Ireland last winter such as Bramblings, Lesser Whitethroats, Black Redstarts, Snow Buntings and Ring-necked Parakeets.
Getting involved in the survey
The value of an individual’s participation in the Irish Garden Bird Survey is not dependent on their bird knowledge, location or garden size but rather, their willingness to get involved every winter. “The value of the survey is when people do it year after year because we can monitor the change then. It doesn’t matter if you have three species in your garden and someone else has 30, we want to find out how those three species fare over time. That is the real crux of the survey,” explains Brian. “We want to hear from people with and without feeders. We want results from every type of garden in the country so that the survey results are representative of the whole country.”Goldfinch. Photo: Dick Coombes.
The Irish Garden Bird Survey is once again sponsored by Ballymaloe, whose support in recent years has helped ensure the survey has gone from strength to strength, improving monitoring at national level and allowing for greater focus on conservation issues facing individual species. “United in our commitment to the environment and inspired by the legacy of our forefather, Ivan Allen, Ballymaloe businesses as a group proudly sponsor BirdWatch Ireland's annual Irish Garden Bird Survey. Mr Ivan Allen, the husband of Myrtle Allen and a devoted lover of birdlife, cherished the natural habitat around Ballymaloe House, and practised sustainable farming way ahead of his time. In his memory, our collective support for the Irish Bird Survey reflects our ongoing celebration of Mr Allen's passion for birdlife and commitment to conservation,” said Marketing and Digital Manager at Ballymaloe House Hotel, Helen Cuddigan. “Together Ballymaloe House Hotel, the Ballymaloe Cookery School and Ballymaloe Foods are honoured to contribute towards supporting the preservation of Irish birdlife via BirdWatch Ireland's important national Irish Garden Bird Survey initiative in his name. We encourage as many households as possible to get involved, every entry helps BirdWatch Ireland protect birdlife on the island of Ireland.” Participating in the Irish Garden Bird Survey each winter is a simple and effective way of contributing to a crucial body of data that will help to guide conservation. Through taking part, you are also sure to reap many rewards as the survey offers an opportunity to increase your bird knowledge, take a daily pause and perhaps, create memorable moments with friends and family. The Irish Garden Bird Survey will kick off on Monday, November 27th. For instructions on how to take part, see the Irish Garden Bird Survey page on our website here.
Large influx of Scandinavian finches to Irish gardens last winter. The Irish Garden Bird Survey has begun again!
BirdWatch Ireland’s Irish Garden Bird Survey returns next week, for the 34th consecutive winter. The survey is very simple and asks people to spend a short amount of time each week watching their garden birds and recording what they see. It plays an important role in tracking the fortunes of some of Ireland’s best-loved wildlife.
On Their Way
BirdWatch Ireland has received lots of correspondence from concerned people all around the country whose garden birds are ‘missing’. This is simply a result of the abundance of natural food available to them in the countryside, but as the weeks go on and weather gets colder more and more birds will be retreating to gardens for food and shelter, just in time for the Irish Garden Bird Survey!
Rare Arrivals
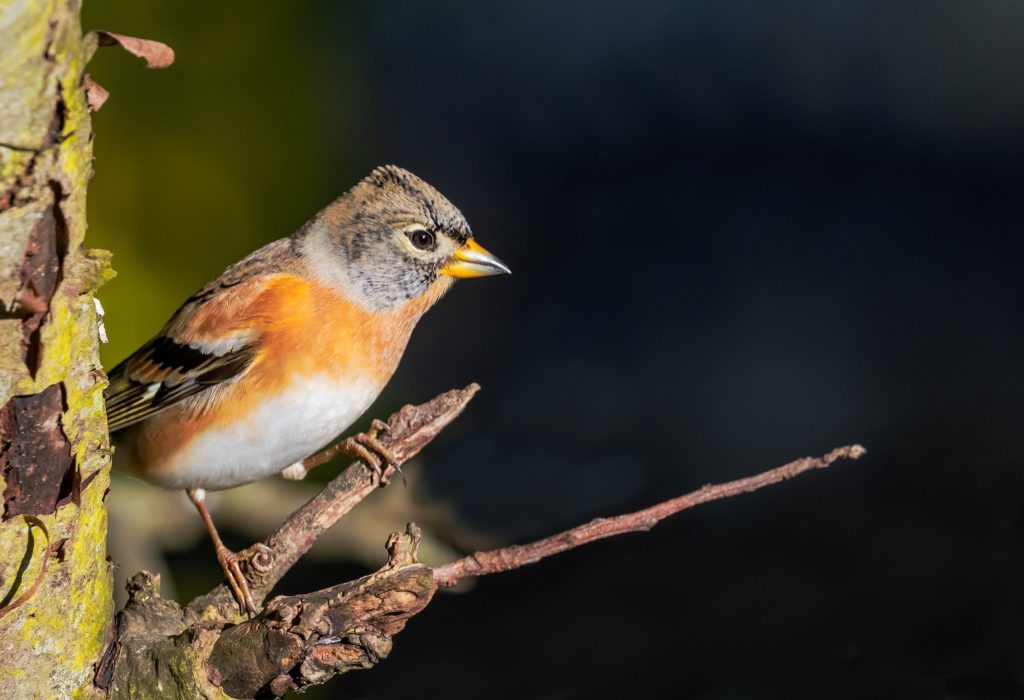
Last winter there was a big increase in the number of Bramblings in Irish gardens. Bramblings are a close relative of our native Chaffinch that breed in northern Scandinavia and are quite rare in Ireland. Every few years however, we get a big influx, and last year 4% of gardens in 21 counties had at least one of these Scandinavian migrants hiding amongst their Chaffinches. “There was a noticeable spike in their numbers in mid-January, corresponding with the lowest recorded temperatures of the winter, highlighting just how important it is to put out food and water in advance of frost or snow!” said Brian Burke, who coordinates the survey for Birdwatch Ireland.

Other notable rarities include the invasive Ring-necked Parakeets in a select few Dublin gardens and a Rustic Bunting in a garden in County Down. Rustic Buntings nest in woodlands in eastern Scandinavia and Siberia and spend the winter in south-east Asia, and this was only the 23rd record of the species in Ireland. A Mediterranean Gull in a Dublin garden represents only the third record of the species in the Irish Garden Bird Survey, though they’re definitely increasing in coastal habitats.

“Taking part in the survey is really easy, and while it doesn’t require a huge commitment, it definitely provides people with extra motivation to keep an even closer eye on their garden birds, and that’s when you might spot something new,” said Brian. “It might be something rare at a national level, or something common but that you’ve never seen in your garden before. There’s excitement either way!”
Common Species, increases and decreases
Robins were seen in the highest proportion of gardens last winter (>99%), followed by Blackbird (>97%) and Blue Tit (>96%), with Magpie moving up to fourth place (90%). House Sparrows were the most numerous birds recorded (average count of 9-10 per garden), followed by Starling and Goldfinch (8-9 per garden).
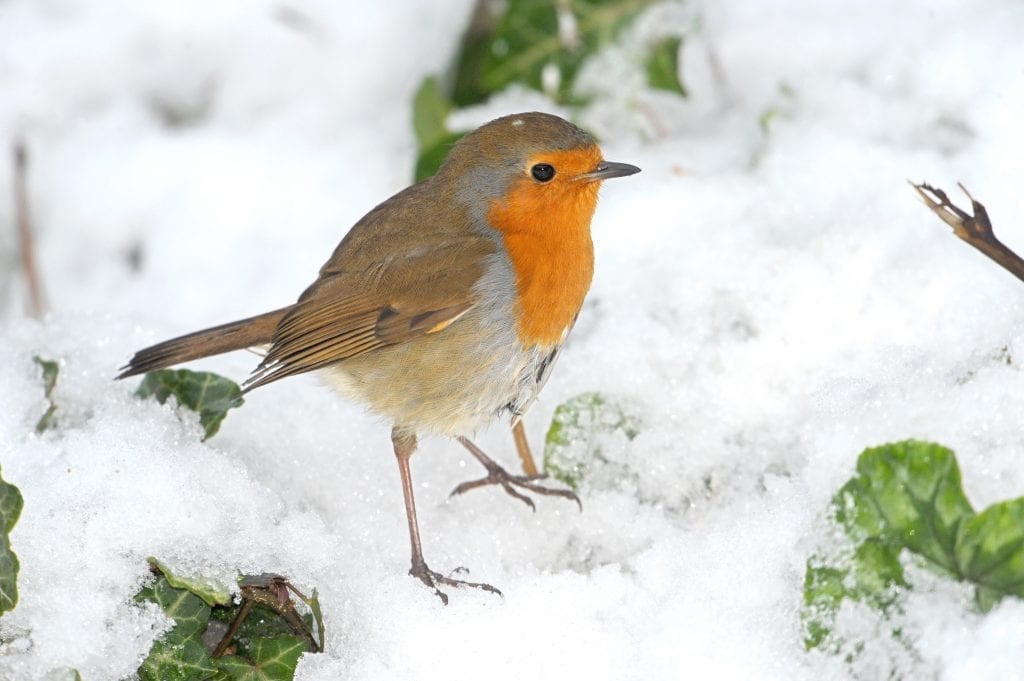

Our native hibernicus subspecies of Coal Tit fell to its worst ranking in 20 years (11th place, <80% of gardens) after a series of poor years. Another species showing significant decreases was Song Thrush (down 10%, from 13th to 17th), which may have suffered high nest losses because of the cold start to the summer the previous year. Pied Wagtail, also known by many as the ‘Willy Wagtail’, also declined by 10%.
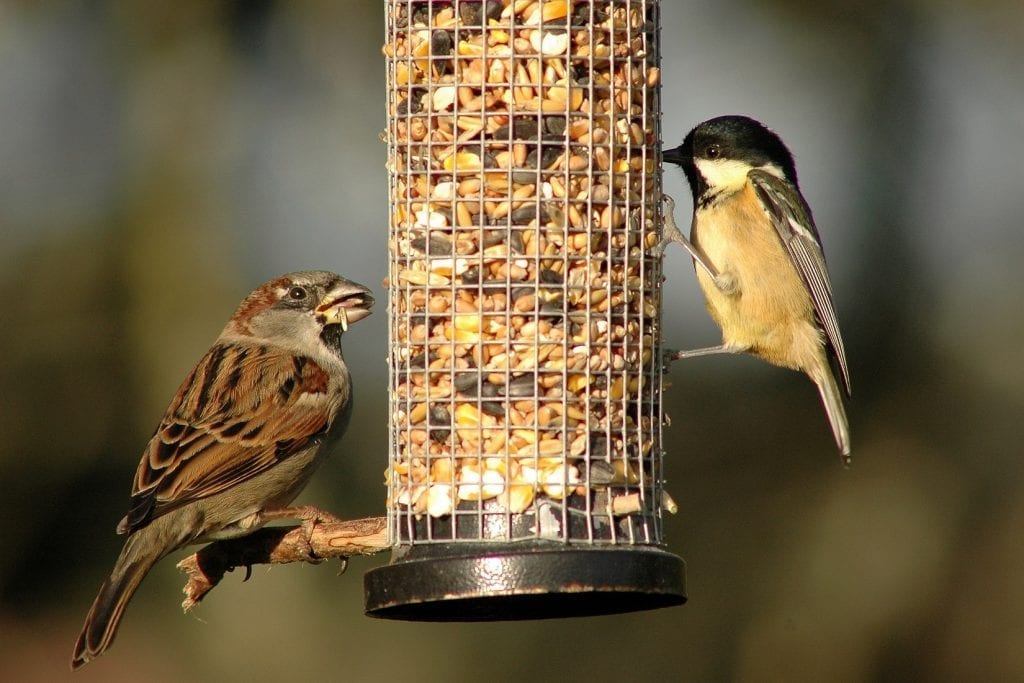

Notable increases include the Jay, a colourful member of the crow family which also belongs to a unique Irish hibernicus subspecies. They were recorded in more than 10% of gardens for the first time ever, reflecting a widespread increase in the Irish population. More common members of the crow family, such as Jackdaw, Rook and Hooded Crow all increased last year, as did all three of our most common pigeon species: Woodpigeon, Collared Dove and Feral Pigeon. Great Spotted Woodpeckers, which first began their colonisation of Ireland around 2005, were recorded in 5% of Irish gardens, across 21 counties, and continue to increase across the country, favouring peanut feeders in the winter.
Avian Flu and Trichomonosis in Garden Birds
BirdWatch Ireland would like to stress that the risk of Avian Flu in garden birds is very low at present and that it is safe to continue to feed your garden birds. Avian Flu decimated some seabird species such as Gannet this summer, with hundreds of dead and unwell birds washing up on beaches, while in more recent months it has been swans, geese and ducks that have been infected. “Bird flu is currently circulating in our waterbird species, but these birds don’t tend to interact closely with garden birds. Swans and sparrows don’t hang out together, so it’s unlikely bird flu will be brought into gardens. It’s a situation we’ll continue to keep a close eye on, however,” said Brian.
The main risk to garden birds continues to be the trichomonas parasite, which has been infecting finches for over 15 years now. Greenfinches were present in fewer than half of gardens last winter, down from over 90% of gardens in the early 2000’s. Also, Chaffinches in urban areas are declining faster than those in rural parts of the country, apparently because there are more feeders in urban gardens where they pick up the infection. “If you’re putting out feeders, you also have a responsibility to clean them thoroughly at least once a week to ensure the costs don’t outweigh the benefits to the birds,” notes Brian.

Supporting the Survey
The Irish Garden Bird Survey is once again sponsored by Ballymaloe, whose support in recent years has helped ensure the survey has gone from strength to strength, improving monitoring at national level and allowing for greater focus on conservation issues facing individual species.

"Collectively Ballymaloe House, Ballymaloe Cookery School and Ballymaloe Foods are delighted to sponsor the Irish Garden Bird Survey annually in memory of our founder Ivan Allen. Ivan, Myrtle Allen's husband, loved the birdlife in and around Ballymaloe House and farmed considerately ensuring their natural habitat was undisturbed. His sustainable farming practices were undoubtedly ahead of their time. Supporting this Irish Garden Bird Survey is Ballymaloe businesses way to continually celebrate Ivan's passion for birdlife, whilst supporting Irish birdlife conservation in his name." Laura Behan, General Manager of Ballymaloe House.
To find out more about the survey and the different trends and patterns seen for different garden birds over the last 30 years, listen to the survey coordinator Brian Burke talk to Ricky Whelan and Niall Hatch for the 'In Your Nature' podcast, by clicking here.

For full details about the survey, how to take part and looking after your garden birds, click here.