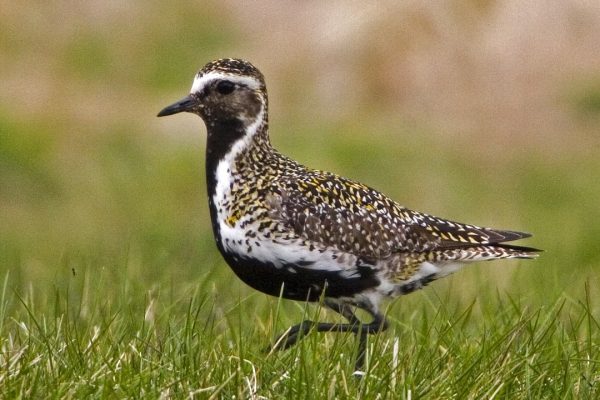
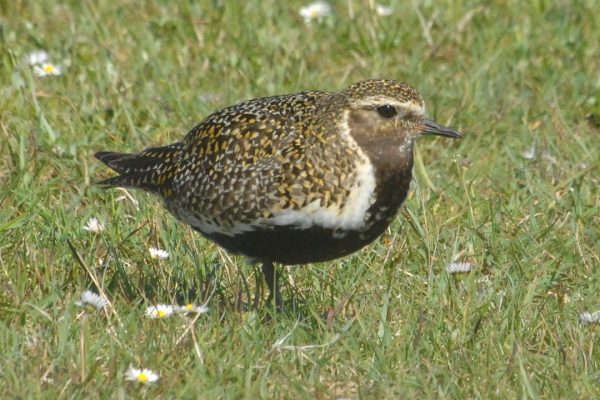
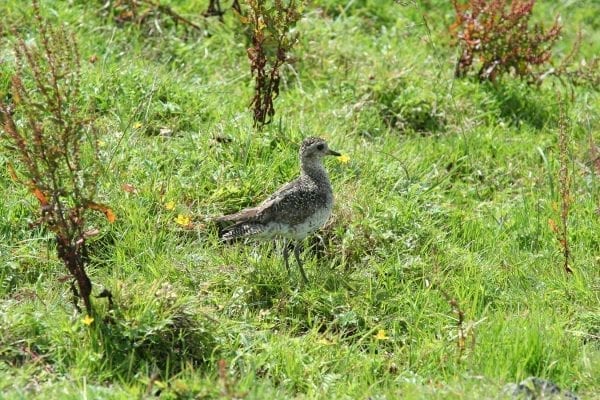
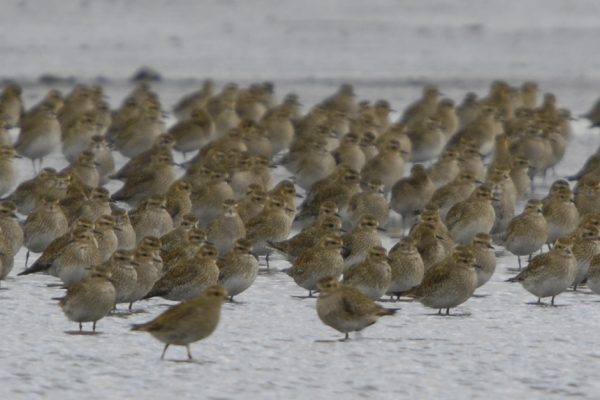
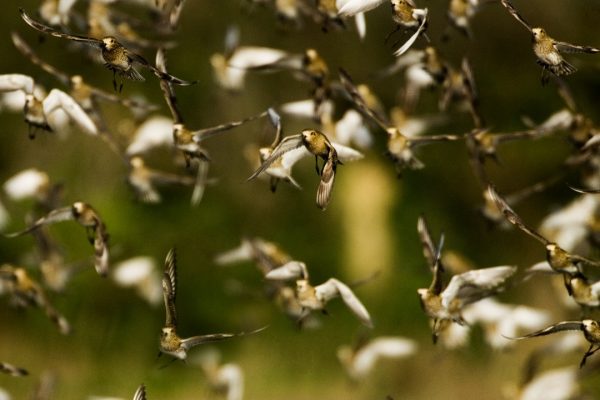
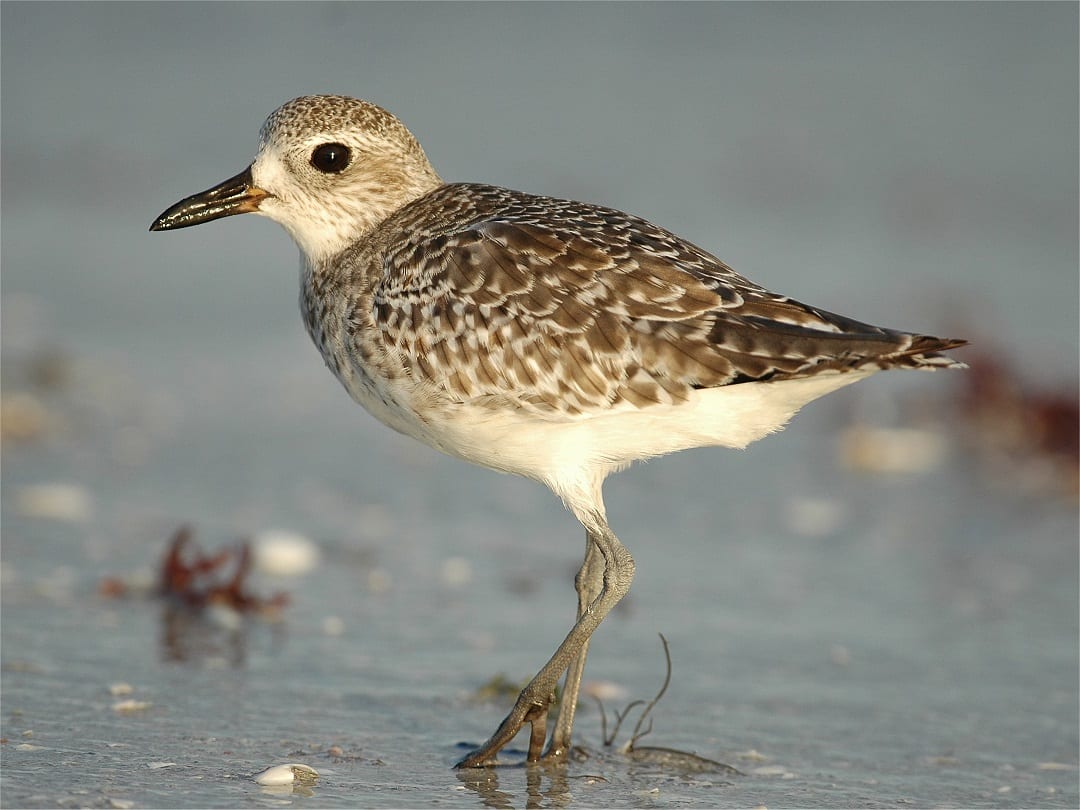
Golden Plover
| Irish Name: | Feadóg bhuí |
| Scientific name: | Pluvialis apricaria |
| Bird Family: | Waders |
red
Conservation status
Conservation status
Status
Summer visitor from France & Iberia (though possibly some remain year-round in Ireland) & winter visitor from Iceland. Most in Ireland between October & February
Identification
Smaller than Grey Plover, with narrower, more pointed wings. Golden brown upperparts, which look grey at close range. Males in summer have more black below than females - extends from throat, towards each eye, and ventrally under neck, chest and belly. In winter, males and females similar in appearence, with no black underparts.
Voice
Flat whistle 'puu' in flight or when alarmed. Rythmic song 'pu-pee-oo' repeated in display flight, often followed by a repeated 'perpurrlya' when alighting, or when on the ground.
Diet
Feed on a variety of soil and surface-living invertebrates, principally beetles and earthworms, but also on plant material such as berries, seeds and grasses. They regularly feed in association with Lapwing & Black-headed Gulls.
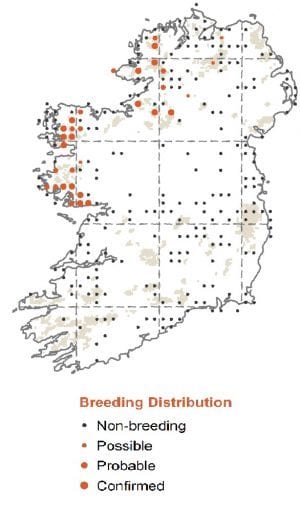
Breeding
Breed in heather moors, blanket bogs & acidic grasslands. Distribution limited to the uplands of northwest counties in Ireland.
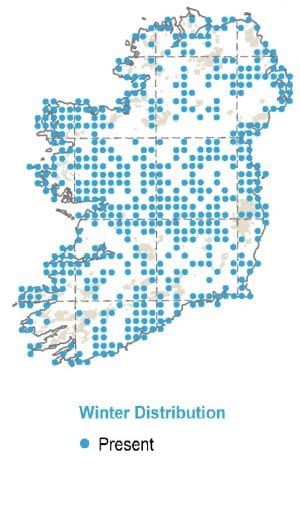
Wintering
Throughout the winter, Golden Plovers are regularly found in large, densely-packed flocks, and in a variety of habitats, both coastal and inland. Their distribution is widespread in Ireland.
Monitored by
Blog posts about this bird

BirdWatch Ireland welcomes the scrapping of the winter stubble rule
BirdWatch Ireland is pleased that the rule for shallow cultivation of winter stubbles has been scrapped in the latest iteration of the Nitrates Action Programme. It is regrettable, however, that this decision was not made sooner, and particularly before farmers cultivated stubble grounds in 2025, leaving threatened bird species looking for other food supplies this winter. In the medium and long term, Ireland’s Common Agriculture Policy Strategic Plan and National Restoration Plan must incentivise farmers to provide sufficient quantity and quality of habitats to restore both wintering and breeding farmland bird populations.
The controversial winter stubble rule was introduced in 2022, despite vociferous opposition from BirdWatch Ireland on account of the risk of severe impacts to farmland birds over the winter months, when food supplies for many Red- and Amber-Listed Birds of Conservation Concern in Ireland are in short supply.
The stubble fields left after crops have been harvested often harbour spilled seeds, which seed-eating birds, such as the Yellowhammer and the Skylark, and rodents will consume during the cold winter. These small birds and mammals are prey species for other birds, including the Hen Harrier, a highly protected and increasingly rare bird of prey that is experiencing ongoing declines. In our submission to government at that time, we highlighted that 30 Red- or Amber-Listed Birds of Conservation in Ireland relied on winter stubbles for food.



Launch of 45th edition of Irish Birds
The status of Greylag Geese in the Republic of Ireland, mapping of farmland bird hotspots and wintering waterbird trends in Ireland are just some of the many topics covered in the latest edition of Irish Birds.
Published in September 2023, the 45th edition of Ireland’s only ornithological journal is now available for purchase from the BirdWatch Ireland shop and would make the perfect gift for anyone with an interest in birds in Ireland and the latest research in the field of ornithology.
The latest edition of Irish Birds includes an overview of site-level and national trends for 35 wintering waterbird species at the 97 Irish Wetland Bird Survey sites. Across all sites analysed between 1994/95 and 2019/2020, Pochard, Scaup, Goldeneye, Golden Plover, Grey Plover and Lapwing showed large declines of over 50%, while Dunlin and Curlew showed moderate declines. 12 species underwent intermediate declines and the remaining 15 species were stable/ increasing. Further research to determine the drivers of these increases and declines is crucial and will help to shape future conservation efforts.
Farmland birds are one of the most threatened species groups in Europe and many studies have highlighted the declines in population and range of farmland birds in Ireland, the UK and across Europe. The declines, which are affecting sub-groups such as breeding waders and other ground-nesting birds in particular, are attributed to habitat loss and fragmentation, agricultural intensification, land drainage, afforestation and increases in predation. Recognising the important role that agri-environment schemes play in protecting and supporting farmland birds, BirdWatch Ireland has developed a series of maps which illustrate Irish hotspots for 28 species, including Curlew, Lapwing and Yellowhammer. These maps and the methods behind them are included and discussed in another paper – ‘Mapping of Farmland Bird Hotspots: a method to assist targeting of agri-environment measures’ – in the latest edition of Irish Birds.
An assessment of the status Greylag Geese in Ireland during the winter from 2017/18 to 2019/20 showed that the Icelandic population has declined by 42% since the previous assessment in 2007/08. This figure coincides with a c. 45% decline in the flyway population over the same period. Despite these population declines, the distribution of Icelandic Greylag Geese has remained unchanged in the Republic of Ireland over the last 10-12 years, with its concentration being in the eastern half of the country. Meanwhile, the feral population of Irish-breeding Greylag Geese is estimated to have increased by between 109 and 147% since 2008. This study, which was conducted by BirdWatch Ireland in collaboration with the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS), can be read in Irish Birds. To conclude, this paper offers recommendations on how monitoring of Greylag Geese can be expanded upon and improved to help to increase our understanding of this species in Ireland.
Another incredibly informative read is a review paper that looks at the status of birds in County Cork. This paper is a summary of the incredibly detailed book, The Birds of County Cork, by Patrick Smiddy, Mark Shorten and Russ Heselden, which provides a comprehensive account of the ecology of all species known to have occurred in Cork from the earliest times to the present.
Notes on topics such as trichomonosis in finch species and nocturnal migration are some of the other interesting things that owners of Irish Birds can delve into.
The journal also includes a book of abstracts from the 2023 Ornithological Research Conference at University College Cork (UCC) and the Irish Rare Birds Report 2021. The latter is published on behalf of the Irish Rare Birds Committee (IRBC) – a group operating under the auspices of BirdWatch Ireland that is responsible for maintaining a list of the birds recorded in the Republic of Ireland, along with “at sea” records. The Irish Ringing Report 2021, which summarises birds ringed and caught in Ireland in 2021, is also included in the latest Irish Birds. There were many unusual discoveries, including a Kingfisher found in Tallaght which was previously sighted in East Sussex earlier in the year. Such long-distance movements of Kingfishers, especially overseas, are rare. There are also numerous examples of birds that reached a high age, including a Great Tit that was just one month shy of the British Trust for Ornithology (BTO) longevity record of 10 years 5 months and 18 days when it was re-trapped in Edenderry in 2021.
As the number one ornithological journal in Ireland, Irish Birds is a necessity for all serious birdwatchers and scientists working in the Irish conservation sector. The 45th edition of Irish Birds is now available from the BirdWatch Ireland shop, both online and in Kilcoole. Should you choose to support BirdWatch Ireland as a key member, you will receive a copy in addition to three copies of our membership magazine, Wings, every year.
Also, for those seeking previous issues, we have plenty of back issues of Irish Birds available at a reduced price. Whether you are keen to complete a collection or simply have a particular interest in a certain year or study, you can contact us to find out more about purchasing back issues.