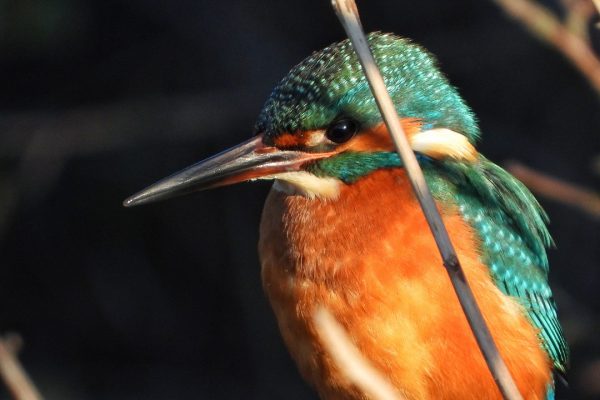
Kingfisher
| Irish Name: | Cruidín |
| Scientific name: | Alcedo atthis |
| Bird Family: | Kingfisher |
amber
Conservation status
Conservation status
Status
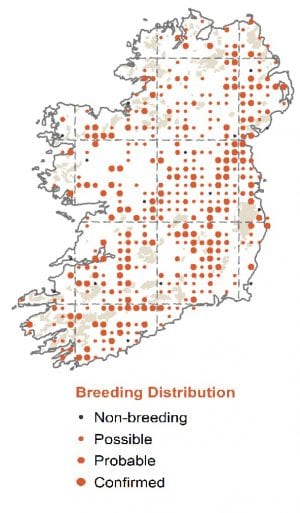
Resident on Irish streams, rivers and canals.
Identification
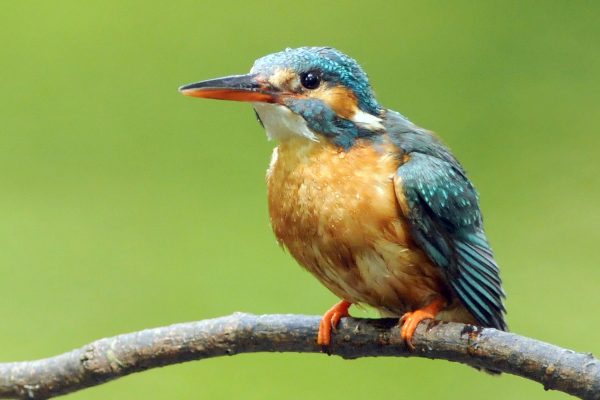
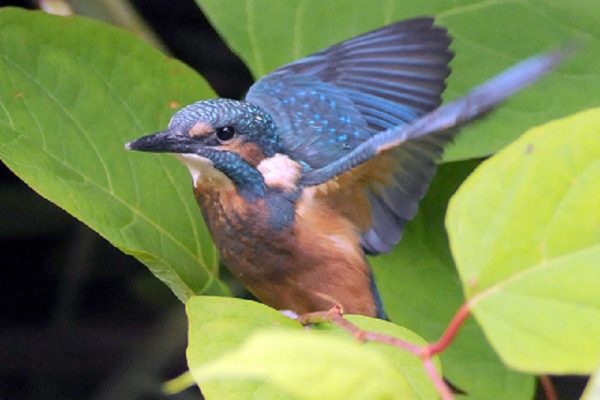
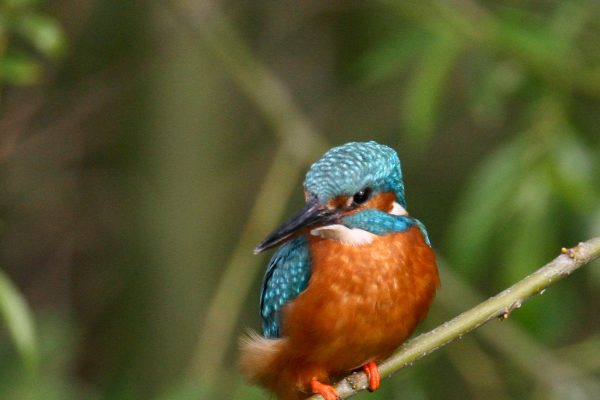
Very distinctive when seen well with its brightly-coloured plumage. The underparts are a bright orange-red, while the wings and back of the head are dark blue. The back, rump and tail are a bright, almost "electric" blue and usually draw attention to a flying bird. Despite these bright colours, can be easily overlooked perched motionless on a branch beside a stream or river on the look-out for fish. During the breeding season, females have a small red patch at the base of the bill, which is not shown by adult males.
Voice
A shill whistled “chee-kee”, frequently repeated. It is usually one first signs that a Kingfisher is present along a stream or river.
Diet
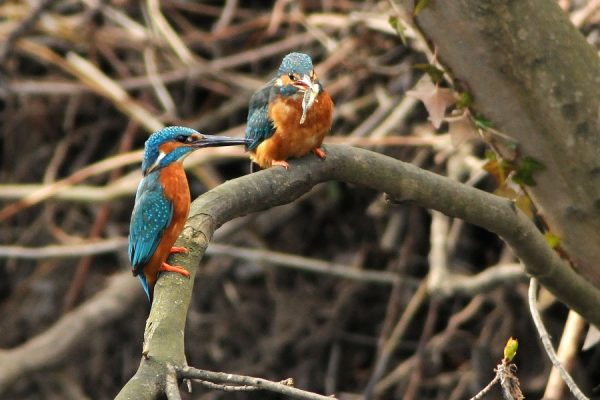
Various species of small fish (Stickleback, Minnow, and Chub) and larger aquatic insects caught by plunge-diving from a perch or while hovering.
Breeding
Kingfishers breed in tunnels dug in vertical banks along streams and rivers.
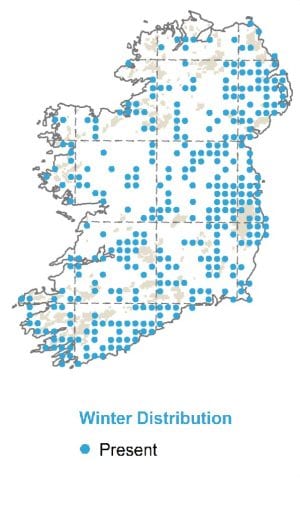
Wintering
A very sedentary species, Kingfishers rarely move from their territories. However, some may move to lakes and coasts during extended spells of poor weather.
Monitored by
Waterways Bird Survey.
Blog posts about this bird
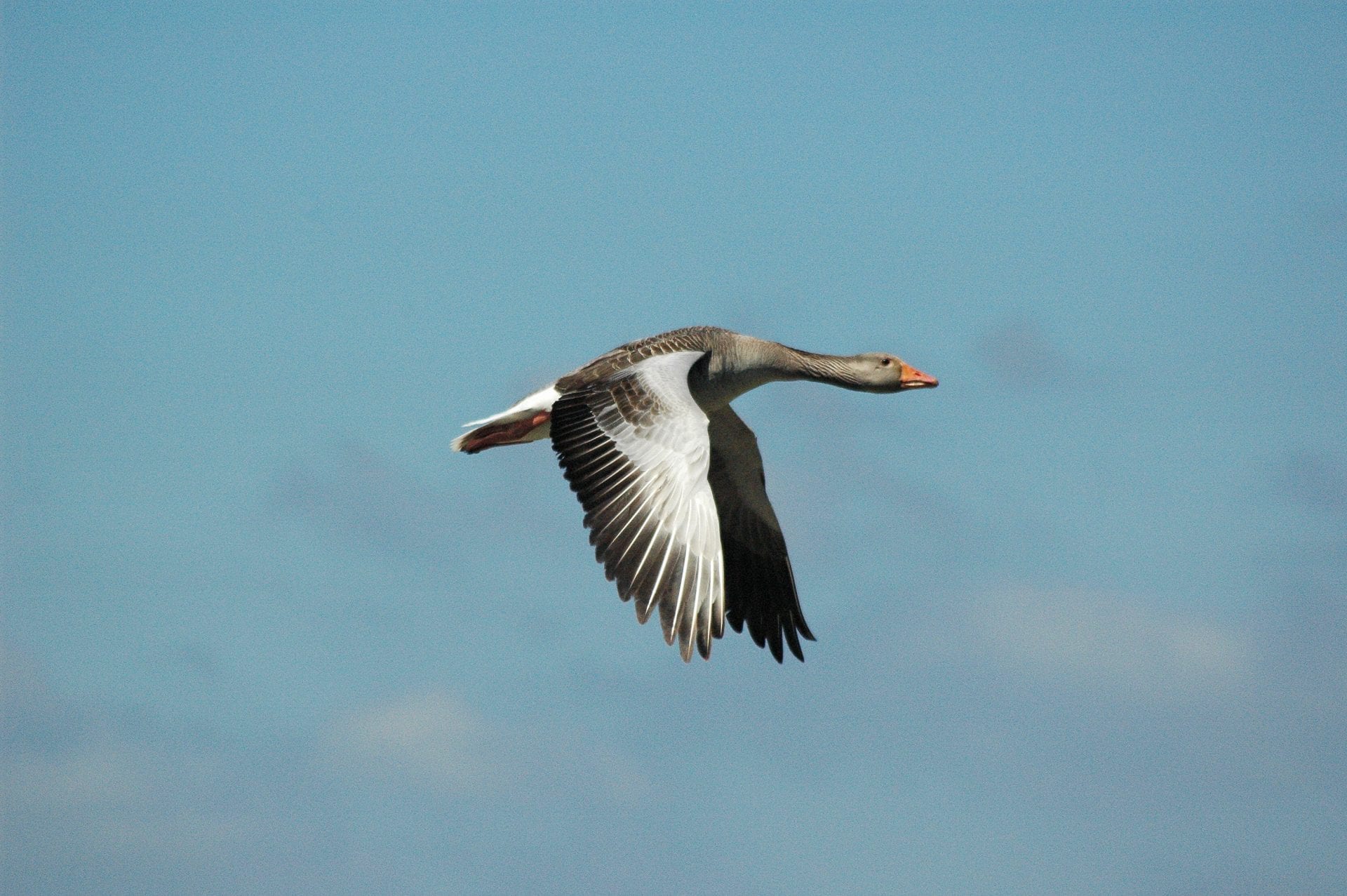

Launch of 45th edition of Irish Birds
The status of Greylag Geese in the Republic of Ireland, mapping of farmland bird hotspots and wintering waterbird trends in Ireland are just some of the many topics covered in the latest edition of Irish Birds.
Published in September 2023, the 45th edition of Ireland’s only ornithological journal is now available for purchase from the BirdWatch Ireland shop and would make the perfect gift for anyone with an interest in birds in Ireland and the latest research in the field of ornithology.
The latest edition of Irish Birds includes an overview of site-level and national trends for 35 wintering waterbird species at the 97 Irish Wetland Bird Survey sites. Across all sites analysed between 1994/95 and 2019/2020, Pochard, Scaup, Goldeneye, Golden Plover, Grey Plover and Lapwing showed large declines of over 50%, while Dunlin and Curlew showed moderate declines. 12 species underwent intermediate declines and the remaining 15 species were stable/ increasing. Further research to determine the drivers of these increases and declines is crucial and will help to shape future conservation efforts.
Farmland birds are one of the most threatened species groups in Europe and many studies have highlighted the declines in population and range of farmland birds in Ireland, the UK and across Europe. The declines, which are affecting sub-groups such as breeding waders and other ground-nesting birds in particular, are attributed to habitat loss and fragmentation, agricultural intensification, land drainage, afforestation and increases in predation. Recognising the important role that agri-environment schemes play in protecting and supporting farmland birds, BirdWatch Ireland has developed a series of maps which illustrate Irish hotspots for 28 species, including Curlew, Lapwing and Yellowhammer. These maps and the methods behind them are included and discussed in another paper – ‘Mapping of Farmland Bird Hotspots: a method to assist targeting of agri-environment measures’ – in the latest edition of Irish Birds.
An assessment of the status Greylag Geese in Ireland during the winter from 2017/18 to 2019/20 showed that the Icelandic population has declined by 42% since the previous assessment in 2007/08. This figure coincides with a c. 45% decline in the flyway population over the same period. Despite these population declines, the distribution of Icelandic Greylag Geese has remained unchanged in the Republic of Ireland over the last 10-12 years, with its concentration being in the eastern half of the country. Meanwhile, the feral population of Irish-breeding Greylag Geese is estimated to have increased by between 109 and 147% since 2008. This study, which was conducted by BirdWatch Ireland in collaboration with the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS), can be read in Irish Birds. To conclude, this paper offers recommendations on how monitoring of Greylag Geese can be expanded upon and improved to help to increase our understanding of this species in Ireland.
Another incredibly informative read is a review paper that looks at the status of birds in County Cork. This paper is a summary of the incredibly detailed book, The Birds of County Cork, by Patrick Smiddy, Mark Shorten and Russ Heselden, which provides a comprehensive account of the ecology of all species known to have occurred in Cork from the earliest times to the present.
Notes on topics such as trichomonosis in finch species and nocturnal migration are some of the other interesting things that owners of Irish Birds can delve into.
The journal also includes a book of abstracts from the 2023 Ornithological Research Conference at University College Cork (UCC) and the Irish Rare Birds Report 2021. The latter is published on behalf of the Irish Rare Birds Committee (IRBC) – a group operating under the auspices of BirdWatch Ireland that is responsible for maintaining a list of the birds recorded in the Republic of Ireland, along with “at sea” records. The Irish Ringing Report 2021, which summarises birds ringed and caught in Ireland in 2021, is also included in the latest Irish Birds. There were many unusual discoveries, including a Kingfisher found in Tallaght which was previously sighted in East Sussex earlier in the year. Such long-distance movements of Kingfishers, especially overseas, are rare. There are also numerous examples of birds that reached a high age, including a Great Tit that was just one month shy of the British Trust for Ornithology (BTO) longevity record of 10 years 5 months and 18 days when it was re-trapped in Edenderry in 2021.
As the number one ornithological journal in Ireland, Irish Birds is a necessity for all serious birdwatchers and scientists working in the Irish conservation sector. The 45th edition of Irish Birds is now available from the BirdWatch Ireland shop, both online and in Kilcoole. Should you choose to support BirdWatch Ireland as a key member, you will receive a copy in addition to three copies of our membership magazine, Wings, every year.
Also, for those seeking previous issues, we have plenty of back issues of Irish Birds available at a reduced price. Whether you are keen to complete a collection or simply have a particular interest in a certain year or study, you can contact us to find out more about purchasing back issues.

BirdWatch Ireland welcomes State purchase of Dowth Estate and establishment of Ireland's seventh National Park
BirdWatch Ireland welcomes the news of the State’s purchase of Dowth Hall demesne in County Meath and the establishment of the 500-acre property as a new National Park.
On Friday, Minister for Housing, Local Government and Heritage, Darragh O Brien TD confirmed the State’s purchase of the World Heritage lands of Dowth Hall and demesne, along with the establishment of a new National Park – the Boyne Valley (Brú na Bóinne) National Park.
A cultural and natural heritage site of national and international importance, the demesne includes Dowth Hall, an eighteenth-century neoclassical country house, and Netterville Manor, a late Victorian almshouse. The lands amount to approximately one-third of the total area of the UNESCO World Heritage Property of Brú na Bóinne, which includes the great Neolithic passage tombs of Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth.
The purchase paves the way for the establishment Ireland’s seventh National Park. It is the second National Park to be established in the east of the country alongside Wicklow Mountains National Park.



Grey Partridge. Photo: Colum Clarke.
Dowth has been actively managed by Devenish Nutrition over the last decade to preserve its cultural heritage and biodiversity. As well as their position within the Brú na Bóinne World Heritage Property, the Dowth lands are important places for nature. They host a wide range of habitats, including species-rich grasslands, native woodlands and mature hedgerows. The Boyne River which runs through the lands is designated as a Special Area of Conservation (SAC) under the Habitats Directive, and as a Special Protection Area (SPA) under the Birds Directive. Following the State purchase, the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) will maintain the careful management of the farmlands, habitats and species to date and will work to protect and improve it even further. The new Boyne Valley (Brú na Bóinne) National Park is rich in bird life. 54 species of birds have been recorded at the site including Red-listed species of conservation concern such as Grey Partridge, Woodcock, Kestrel, Swift and Yellowhammer. 19 species recorded at the site are on the Amber list, including Kingfisher, Common Sandpiper, Cormorant and Little Grebe. Dowth is also a haven for other wildlife and plants. The River Boyne is of national importance for a number of species of bat including Common Pipistrelle, Soprano Pipistrelle, Natterer's Bat, Brown Long-eared Bat, Leisler’s Bat, Whiskered Bat, Daubenton’s bat and Nathusius’ Pipistrelle. It also hosts many species of butterfly including Small Tortoiseshell, Ringlet, Holly Blue, Peacock, Meadow Brown, Speckled Wood, Large White, Green-veined White, Small White, Red Admiral and Painted Lady. While surveys have not been completed, it is likely that a large population of macro-moths (of which there are over 800 species) occur within managed habitats. Seven species of bee have also been recorded here including White-tailed Bumblebee, Honey Bee, Common Carder Bee, Garden Bumblebee, Early Bumblebee, Red-tailed Bumblebee and Buff-tailed Bumblebee.
Woodcock on the nest. Photo: Richard T Mills
Minister for Housing, Local Government and Heritage, Darragh O’Brien TD welcomed the significant purchase and highlighted the many opportunities it could bring. “Rarely does the State get an opportunity to acquire lands of such significance. This landscape and property is of exceptional heritage importance. Here in this one place, we have over 5000 years of recorded history. In our care, it will significantly enhance our management of the Brú na Bóinne World Heritage landscape. We will conserve and protect Dowth’s heritage in line with our obligations to UNESCO and we will enhance responsible tourism, ensuring it becomes a standout destination. This purchase opens up possibilities for us to develop heritage partnerships, protect remarkable heritage and make it accessible. It is simply an outstanding opportunity for an outstanding place.” Minister of State with responsibility for Heritage and Electoral Reform, Malcolm Noonan TD said that the purchase represented an “outstanding addition to Ireland’s family of National Parks”. “We look forward to sustaining and growing this legacy to ensure that farming, nature and the cultural heritage of this ancient landscape can continue in harmony, as they have done since our ancestors first settled in the Boyne Valley over 5,500 years ago. Through our partnerships with state agencies, departments, local authorities and communities – which are enshrined in Heritage Ireland 2030, our national heritage plan – we are committed to nurturing Dowth as a key pillar of Ireland’s remarkable heritage that we can all admire, be proud of and enjoy.” The National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS), the National Monuments Service and the Office of Public Works (OPW) will now work together to deliver a Masterplan for the property that allows for the protection, presentation and management of this area of the Boyne Valley. Management of Dowth Hall and lands will form part of the existing Brú na Bóinne Management Plan and strengthen the vision for the protection of Dowth’s remarkable heritage, including the Neolithic passage tomb discovered in 2017 under Dowth Hall itself. “The work begins now of developing a Masterplan for Dowth. We will approach this with a keen sense of responsibility, ambition and excitement, knowing that this is a remarkable opportunity for Ireland’s heritage to play a lead role in the regional economy and in place-making for the east of the country,” said Niall O Donnchu, Director General of National Parks and Wildlife Service. “This new National Park is a special place where history, heritage, nature and culture collide. We will work with stakeholders in developing a Masterplan that will deliver on its full potential for locals, visitors and generations to come. I want to pay tribute to our team across the National Parks and Wildlife Service and the National Monuments Services for their work on this acquisition, and on their readiness to take over custodianship of this remarkable place from Devenish who have championed and maintained it with such care over the last 16 years.”