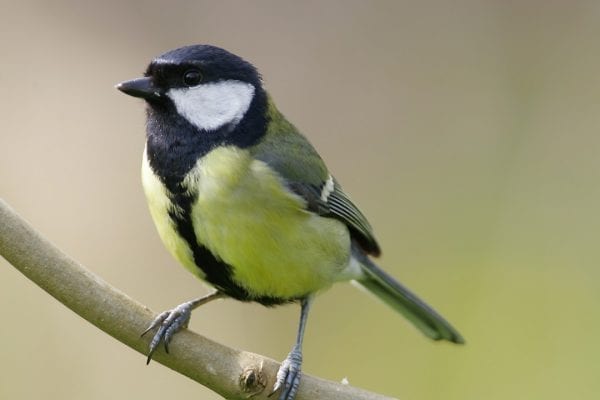
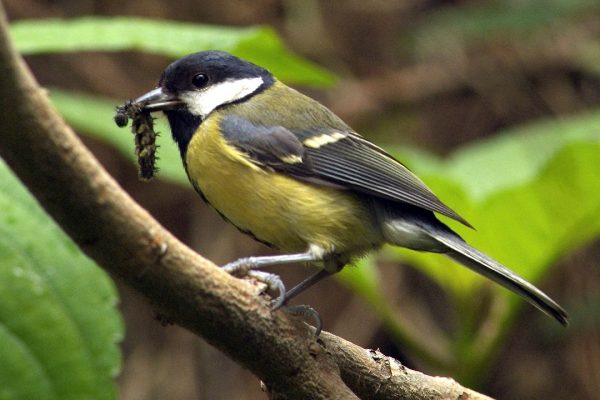
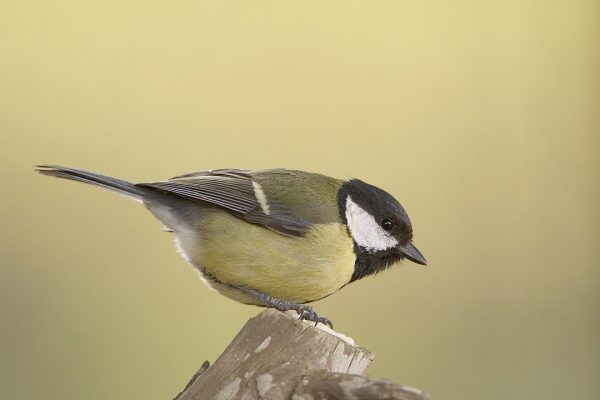
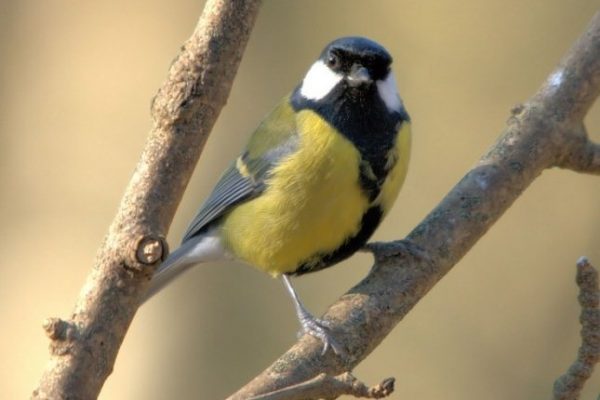
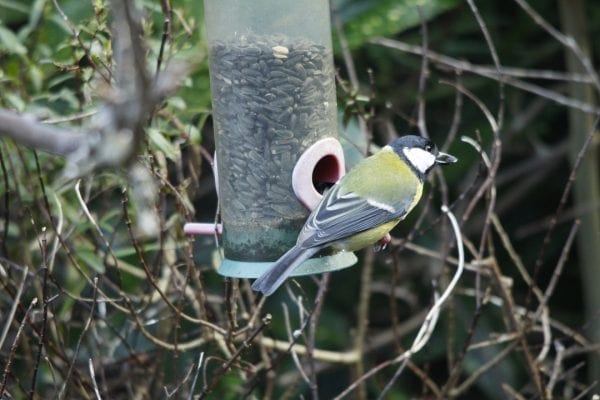
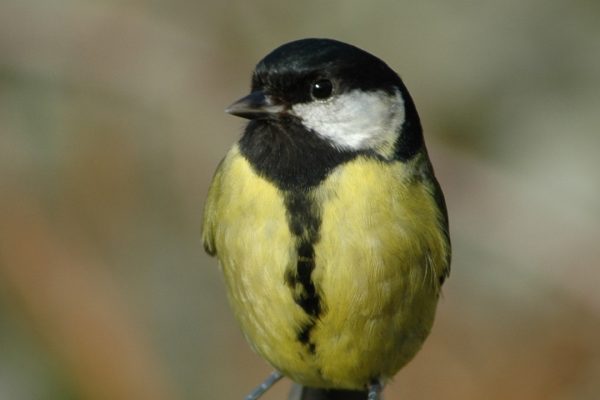
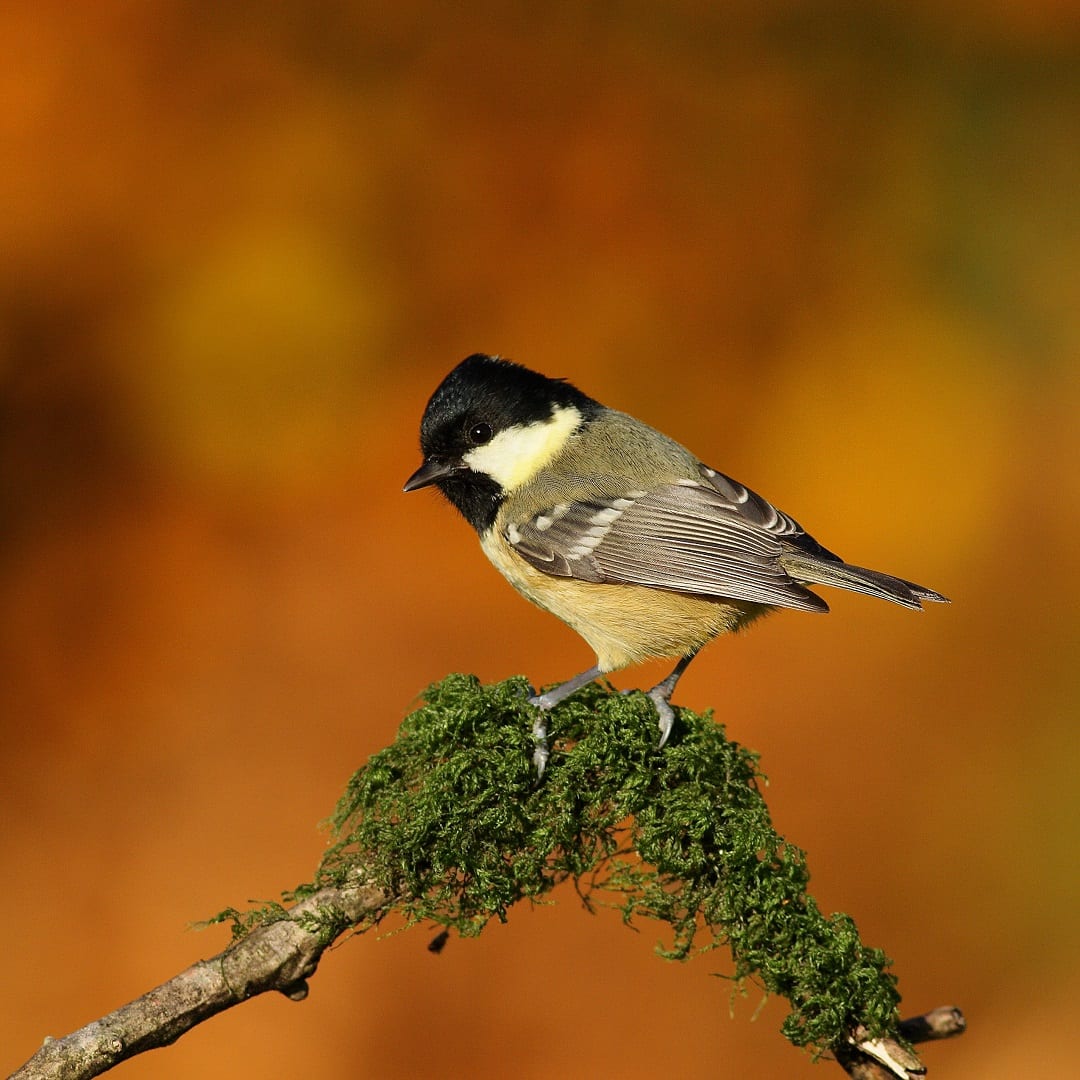
Great Tit
| Irish Name: | Meantán mór |
| Scientific name: | Parus major |
| Bird Family: | Tits |
green
Conservation status
Conservation status
Status
Resident. One of Ireland's top 20 most widespread garden birds.
Identification
The largest of the tit family. Striking black head with large white cheek patches and black band running down the centre of a bright yellow breast. Back yellowish- green, wings and tail silvery blue. In flight, white outer tail feathers show. When perched, a distinct white wingbar shows. Bill is pointed but stout, legs bluish-grey.
Voice
Typical song a loud, full "teacher, teacher" and many other variations. Call a scolding sound or a quiet, repeated " tew, tew tew".
Diet
Mainly insects, seeds and nuts. Will use peanut feeders and take scraps on bird tables.
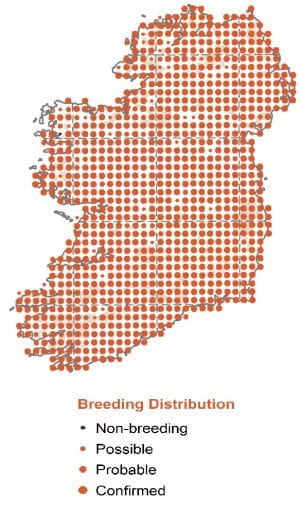
Breeding
Breeds throughout Ireland - prefers broad-leaved woodland, but also in farmland, parks and gardens. Nests in cavity in tree or wall. Often choosing unusual site such as a pipe or letterbox. Readily uses nestboxes.
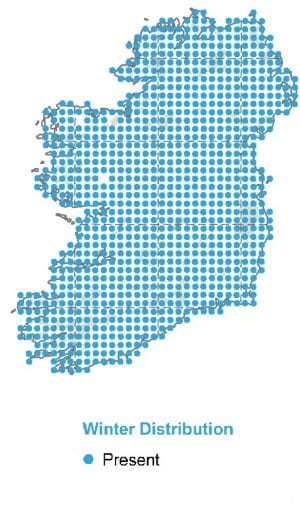
Wintering
Widespread.
Monitored by
Blog posts about this bird

Launch of 45th edition of Irish Birds
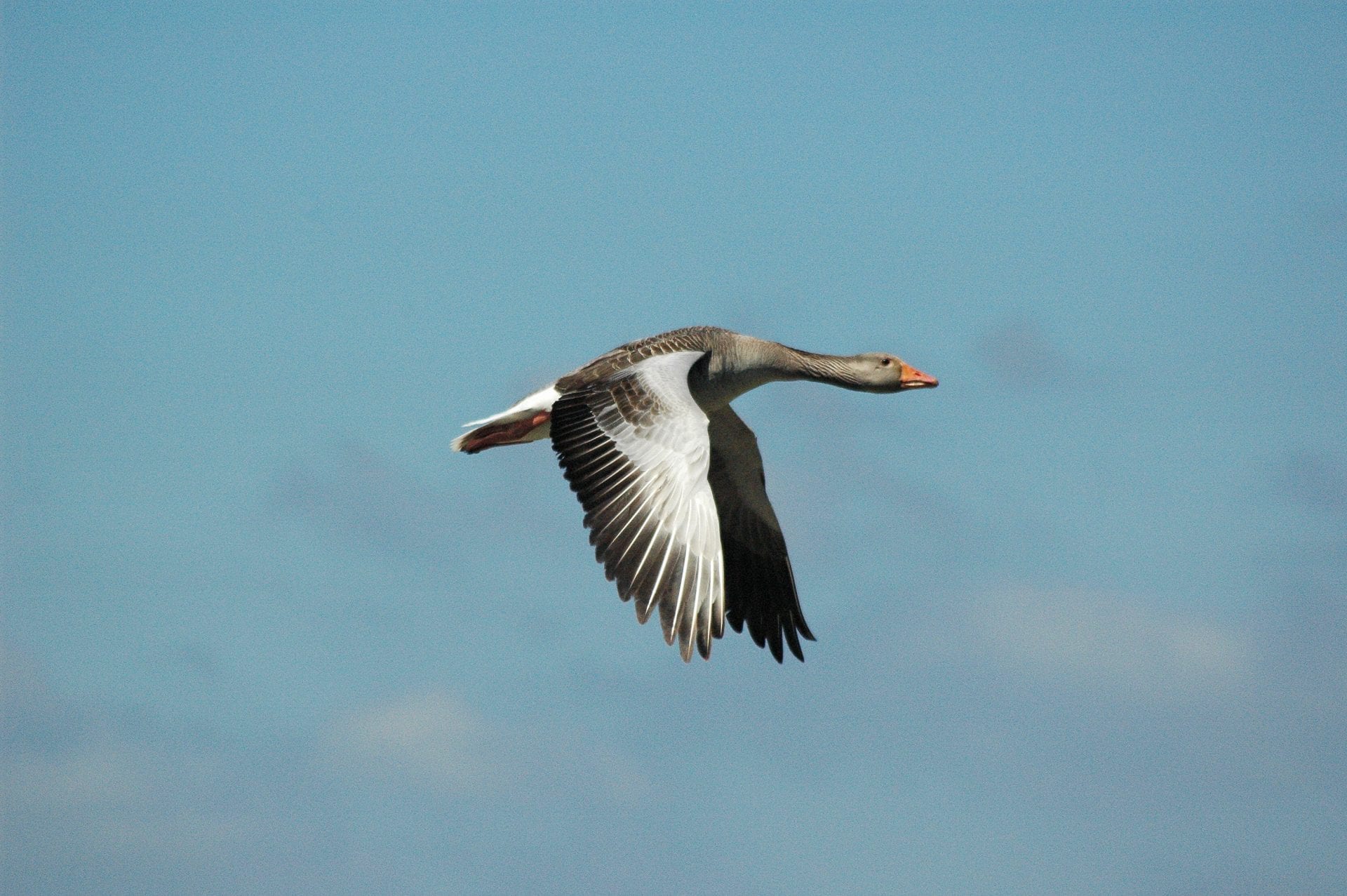
The status of Greylag Geese in the Republic of Ireland, mapping of farmland bird hotspots and wintering waterbird trends in Ireland are just some of the many topics covered in the latest edition of Irish Birds.
Published in September 2023, the 45th edition of Ireland’s only ornithological journal is now available for purchase from the BirdWatch Ireland shop and would make the perfect gift for anyone with an interest in birds in Ireland and the latest research in the field of ornithology.
The latest edition of Irish Birds includes an overview of site-level and national trends for 35 wintering waterbird species at the 97 Irish Wetland Bird Survey sites. Across all sites analysed between 1994/95 and 2019/2020, Pochard, Scaup, Goldeneye, Golden Plover, Grey Plover and Lapwing showed large declines of over 50%, while Dunlin and Curlew showed moderate declines. 12 species underwent intermediate declines and the remaining 15 species were stable/ increasing. Further research to determine the drivers of these increases and declines is crucial and will help to shape future conservation efforts.
Farmland birds are one of the most threatened species groups in Europe and many studies have highlighted the declines in population and range of farmland birds in Ireland, the UK and across Europe. The declines, which are affecting sub-groups such as breeding waders and other ground-nesting birds in particular, are attributed to habitat loss and fragmentation, agricultural intensification, land drainage, afforestation and increases in predation. Recognising the important role that agri-environment schemes play in protecting and supporting farmland birds, BirdWatch Ireland has developed a series of maps which illustrate Irish hotspots for 28 species, including Curlew, Lapwing and Yellowhammer. These maps and the methods behind them are included and discussed in another paper – ‘Mapping of Farmland Bird Hotspots: a method to assist targeting of agri-environment measures’ – in the latest edition of Irish Birds.
An assessment of the status Greylag Geese in Ireland during the winter from 2017/18 to 2019/20 showed that the Icelandic population has declined by 42% since the previous assessment in 2007/08. This figure coincides with a c. 45% decline in the flyway population over the same period. Despite these population declines, the distribution of Icelandic Greylag Geese has remained unchanged in the Republic of Ireland over the last 10-12 years, with its concentration being in the eastern half of the country. Meanwhile, the feral population of Irish-breeding Greylag Geese is estimated to have increased by between 109 and 147% since 2008. This study, which was conducted by BirdWatch Ireland in collaboration with the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS), can be read in Irish Birds. To conclude, this paper offers recommendations on how monitoring of Greylag Geese can be expanded upon and improved to help to increase our understanding of this species in Ireland.
Another incredibly informative read is a review paper that looks at the status of birds in County Cork. This paper is a summary of the incredibly detailed book, The Birds of County Cork, by Patrick Smiddy, Mark Shorten and Russ Heselden, which provides a comprehensive account of the ecology of all species known to have occurred in Cork from the earliest times to the present.
Notes on topics such as trichomonosis in finch species and nocturnal migration are some of the other interesting things that owners of Irish Birds can delve into.
The journal also includes a book of abstracts from the 2023 Ornithological Research Conference at University College Cork (UCC) and the Irish Rare Birds Report 2021. The latter is published on behalf of the Irish Rare Birds Committee (IRBC) – a group operating under the auspices of BirdWatch Ireland that is responsible for maintaining a list of the birds recorded in the Republic of Ireland, along with “at sea” records. The Irish Ringing Report 2021, which summarises birds ringed and caught in Ireland in 2021, is also included in the latest Irish Birds. There were many unusual discoveries, including a Kingfisher found in Tallaght which was previously sighted in East Sussex earlier in the year. Such long-distance movements of Kingfishers, especially overseas, are rare. There are also numerous examples of birds that reached a high age, including a Great Tit that was just one month shy of the British Trust for Ornithology (BTO) longevity record of 10 years 5 months and 18 days when it was re-trapped in Edenderry in 2021.
As the number one ornithological journal in Ireland, Irish Birds is a necessity for all serious birdwatchers and scientists working in the Irish conservation sector. The 45th edition of Irish Birds is now available from the BirdWatch Ireland shop, both online and in Kilcoole. Should you choose to support BirdWatch Ireland as a key member, you will receive a copy in addition to three copies of our membership magazine, Wings, every year.
Also, for those seeking previous issues, we have plenty of back issues of Irish Birds available at a reduced price. Whether you are keen to complete a collection or simply have a particular interest in a certain year or study, you can contact us to find out more about purchasing back issues.

Large influx of Scandinavian finches to Irish gardens last winter. The Irish Garden Bird Survey has begun again!
BirdWatch Ireland’s Irish Garden Bird Survey returns next week, for the 34th consecutive winter. The survey is very simple and asks people to spend a short amount of time each week watching their garden birds and recording what they see. It plays an important role in tracking the fortunes of some of Ireland’s best-loved wildlife.
On Their Way
BirdWatch Ireland has received lots of correspondence from concerned people all around the country whose garden birds are ‘missing’. This is simply a result of the abundance of natural food available to them in the countryside, but as the weeks go on and weather gets colder more and more birds will be retreating to gardens for food and shelter, just in time for the Irish Garden Bird Survey!
Rare Arrivals
Last winter there was a big increase in the number of Bramblings in Irish gardens. Bramblings are a close relative of our native Chaffinch that breed in northern Scandinavia and are quite rare in Ireland. Every few years however, we get a big influx, and last year 4% of gardens in 21 counties had at least one of these Scandinavian migrants hiding amongst their Chaffinches. “There was a noticeable spike in their numbers in mid-January, corresponding with the lowest recorded temperatures of the winter, highlighting just how important it is to put out food and water in advance of frost or snow!” said Brian Burke, who coordinates the survey for Birdwatch Ireland.
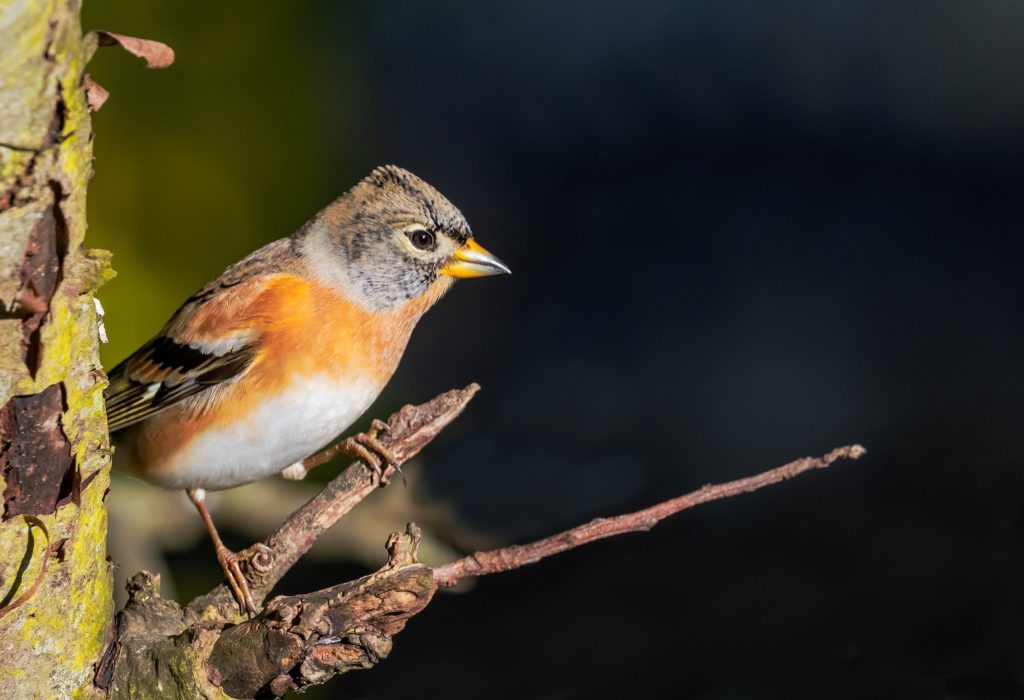

Other notable rarities include the invasive Ring-necked Parakeets in a select few Dublin gardens and a Rustic Bunting in a garden in County Down. Rustic Buntings nest in woodlands in eastern Scandinavia and Siberia and spend the winter in south-east Asia, and this was only the 23rd record of the species in Ireland. A Mediterranean Gull in a Dublin garden represents only the third record of the species in the Irish Garden Bird Survey, though they’re definitely increasing in coastal habitats.

“Taking part in the survey is really easy, and while it doesn’t require a huge commitment, it definitely provides people with extra motivation to keep an even closer eye on their garden birds, and that’s when you might spot something new,” said Brian. “It might be something rare at a national level, or something common but that you’ve never seen in your garden before. There’s excitement either way!”
Common Species, increases and decreases
Robins were seen in the highest proportion of gardens last winter (>99%), followed by Blackbird (>97%) and Blue Tit (>96%), with Magpie moving up to fourth place (90%). House Sparrows were the most numerous birds recorded (average count of 9-10 per garden), followed by Starling and Goldfinch (8-9 per garden).

Our native hibernicus subspecies of Coal Tit fell to its worst ranking in 20 years (11th place, <80% of gardens) after a series of poor years. Another species showing significant decreases was Song Thrush (down 10%, from 13th to 17th), which may have suffered high nest losses because of the cold start to the summer the previous year. Pied Wagtail, also known by many as the ‘Willy Wagtail’, also declined by 10%.

Notable increases include the Jay, a colourful member of the crow family which also belongs to a unique Irish hibernicus subspecies. They were recorded in more than 10% of gardens for the first time ever, reflecting a widespread increase in the Irish population. More common members of the crow family, such as Jackdaw, Rook and Hooded Crow all increased last year, as did all three of our most common pigeon species: Woodpigeon, Collared Dove and Feral Pigeon. Great Spotted Woodpeckers, which first began their colonisation of Ireland around 2005, were recorded in 5% of Irish gardens, across 21 counties, and continue to increase across the country, favouring peanut feeders in the winter.
Avian Flu and Trichomonosis in Garden Birds
BirdWatch Ireland would like to stress that the risk of Avian Flu in garden birds is very low at present and that it is safe to continue to feed your garden birds. Avian Flu decimated some seabird species such as Gannet this summer, with hundreds of dead and unwell birds washing up on beaches, while in more recent months it has been swans, geese and ducks that have been infected. “Bird flu is currently circulating in our waterbird species, but these birds don’t tend to interact closely with garden birds. Swans and sparrows don’t hang out together, so it’s unlikely bird flu will be brought into gardens. It’s a situation we’ll continue to keep a close eye on, however,” said Brian.
The main risk to garden birds continues to be the trichomonas parasite, which has been infecting finches for over 15 years now. Greenfinches were present in fewer than half of gardens last winter, down from over 90% of gardens in the early 2000’s. Also, Chaffinches in urban areas are declining faster than those in rural parts of the country, apparently because there are more feeders in urban gardens where they pick up the infection. “If you’re putting out feeders, you also have a responsibility to clean them thoroughly at least once a week to ensure the costs don’t outweigh the benefits to the birds,” notes Brian.

Supporting the Survey
The Irish Garden Bird Survey is once again sponsored by Ballymaloe, whose support in recent years has helped ensure the survey has gone from strength to strength, improving monitoring at national level and allowing for greater focus on conservation issues facing individual species.

"Collectively Ballymaloe House, Ballymaloe Cookery School and Ballymaloe Foods are delighted to sponsor the Irish Garden Bird Survey annually in memory of our founder Ivan Allen. Ivan, Myrtle Allen's husband, loved the birdlife in and around Ballymaloe House and farmed considerately ensuring their natural habitat was undisturbed. His sustainable farming practices were undoubtedly ahead of their time. Supporting this Irish Garden Bird Survey is Ballymaloe businesses way to continually celebrate Ivan's passion for birdlife, whilst supporting Irish birdlife conservation in his name." Laura Behan, General Manager of Ballymaloe House.
To find out more about the survey and the different trends and patterns seen for different garden birds over the last 30 years, listen to the survey coordinator Brian Burke talk to Ricky Whelan and Niall Hatch for the 'In Your Nature' podcast, by clicking here.

For full details about the survey, how to take part and looking after your garden birds, click here.